PAT(甲級)2019年冬季考試 7-4 Cartesian Tree
7-4 Cartesian Tree (30分)
A Cartesian tree is a binary tree constructed from a sequence of distinct numbers. The tree is heap-ordered, and an inorder traversal returns the original sequence. For example, given the sequence { 8, 15, 3, 4, 1, 5, 12, 10, 18, 6 }, the min-heap Cartesian tree is shown by the figure.算法
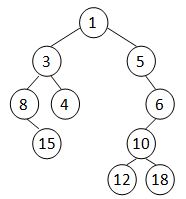
Your job is to output the level-order traversal sequence of the min-heap Cartesian tree.數組
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts from giving a positive integer N (≤30), and then N distinct numbers in the next line, separated by a space. All the numbers are in the range of int.函數
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line the level-order traversal sequence of the min-heap Cartesian tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line.spa
Sample Input:
10 8 15 3 4 1 5 12 10 18 6`
Sample Output:
1 3 5 8 4 6 15 10 12 18
題目限制:

題目大意:
現給定一顆笛卡爾樹的中序序列,它知足小根堆的性質,如今須要輸出其層序遍歷。3d
算法思路:
大體思路就是建樹和層序遍歷,其惟一的難點在於建樹,其實只要知道了根節點的位置就不是問題,首先咱們如今有這顆樹的中序序列,保存在origin數組中,同時使用unordered_map<int,int> pos 保存每個節點在中序序列中的位置,建樹的關鍵是得只要每個子樹的根節點和在中序遍歷中的位置,這裏的子樹都知足小根堆的性質,說明在[inL,inR]之間最小的數字就是當前子樹的根節點,那麼咱們使用getMin得到original中的[left,right]最小的那個數字,代碼以下:code
// 在original的[left,right]中找到最小的那個數字
int getMin(int left,int right){
int Min = 0x3fffffff;
for(int i=left;i<=right;++i){
Min = Min>original[i]?original[i]:Min;
}
return Min;
}
接下來就能夠使用createTree函數來進行建樹了,代碼以下:blog
Node* createTree(int inL,int inR){
if(inL>inR) return nullptr;
Node* root = new Node;
root->data = getMin(inL,inR);
int k = pos[root->data];// 根節點的位置
//[inL,k-1]爲左子樹
root->left = createTree(inL,k-1);
//[k+1,inR]爲右子樹
root->right = createTree(k+1,inR);
return root;
}
最後就是層序遍歷並輸出。ci
注意點:
- 一、結點數值有點偏大,使用數組保存結點的位置會致使段錯誤,使用map比較好
提交結果:

AC代碼:
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
};
int original[40];
unordered_map<int,int> pos;// 每個節點在中序序列中的位置
// 在original的[left,right]中找到最小的那個數字
int getMin(int left,int right){
int Min = 0x3fffffff;
for(int i=left;i<=right;++i){
Min = Min>original[i]?original[i]:Min;
}
return Min;
}
Node* createTree(int inL,int inR){
if(inL>inR) return nullptr;
Node* root = new Node;
root->data = getMin(inL,inR);
int k = pos[root->data];// 根節點的位置
//[inL,k-1]爲左子樹
root->left = createTree(inL,k-1);
//[k+1,inR]爲右子樹
root->right = createTree(k+1,inR);
return root;
}
int num = 0;
void BFS(Node* root){
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()){
Node* t = q.front();
q.pop();
if(num==0){
printf("%d",t->data);
++num;
} else {
printf(" %d",t->data);
}
if(t->left){
q.push(t->left);
}
if(t->right){
q.push(t->right);
}
}
}
int main(){
int N;
scanf("%d",&N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
scanf("%d",&original[i]);
pos[original[i]] = i;
}
Node* root = createTree(0,N-1);
BFS(root);
return 0;
}
- 1. PAT-2018年冬季考試-甲級
- 2. PAT(甲級)2019年冬季考試 7-2 Block Reversing
- 3. PAT(甲級)2019年冬季考試 7-1 Good in C
- 4. PAT(甲級)2019年冬季考試 7-3 Summit
- 5. PAT-2019年春季考試-甲級-Structure of a Binary Tree
- 6. PAT(甲級)2019年春季考試 7-4 Structure of a Binary Tree
- 7. PAT(甲級)2019年秋季考試 7-3 Postfix Expression
- 8. PAT(甲級)2020年秋季考試 7-3 Left-View of Binary Tree
- 9. PAT(甲級)2019年秋季考試 7-4 Dijkstra Sequence
- 10. PAT(甲級)2019年秋季考試 7-1 Forever
- 更多相關文章...
- • Lua 調試(Debug) - Lua 教程
- • Eclipse Debug 調試 - Eclipse 教程
- • 爲了進字節跳動,我精選了29道Java經典算法題,帶詳細講解
- • 算法總結-雙指針
-
每一个你不满意的现在,都有一个你没有努力的曾经。
- 1. PAT-2018年冬季考試-甲級
- 2. PAT(甲級)2019年冬季考試 7-2 Block Reversing
- 3. PAT(甲級)2019年冬季考試 7-1 Good in C
- 4. PAT(甲級)2019年冬季考試 7-3 Summit
- 5. PAT-2019年春季考試-甲級-Structure of a Binary Tree
- 6. PAT(甲級)2019年春季考試 7-4 Structure of a Binary Tree
- 7. PAT(甲級)2019年秋季考試 7-3 Postfix Expression
- 8. PAT(甲級)2020年秋季考試 7-3 Left-View of Binary Tree
- 9. PAT(甲級)2019年秋季考試 7-4 Dijkstra Sequence
- 10. PAT(甲級)2019年秋季考試 7-1 Forever