手寫Promise - 實現一個基礎的Promise
前端開發中常常會用到Promise,不過有部分人並不清楚Promise的原理,本文也是本人在學習Promise時對Promis的一些認識,但願能對各位童鞋有所幫助。javascript
手寫Promise - 實現一個基礎的Promise
[手寫Promise - 實例方法catch、finally]()
[手寫Promise - 經常使用靜態方法all、any、resolve、reject、race]()前端
從認識Promise開始。。。
/* 模擬一個簡單的異步行爲 */
function fetchData() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('willem');
}, 1000);
});
}
fetchData().then((data) => {
// after 1000ms
console.log(data); // willem
return 'wei';
}, (err) => {}).then((data2) => {
console.log(data2); // wei
});
上面的例子算是一個最多見的用法,可能在使用的時候更多的使用的是catch來處理異常來替代then方法的第二個參數,但catch也只是一個then的語法糖。java
從中咱們能夠用一些句子來描述Promise。git
- promise是一個類,它的構造函數接受一個函數,函數的兩個參數也都是函數
- 在傳入的函數中執行resolve表示成功,執行reject表示失敗,傳入的值會傳給then方法的回調函數
- promise有一個叫作then的方法,該方法有兩個參數,第一個參數是成功以後執行的回調函數,第二個參數是失敗以後執行的回調函數。then方法在resolve或者reject執行以後纔會執行,而且then方法中的值是傳給resolve或reject的參數
- promise支持鏈式調用
有了相應的描述,接下來就是來一步一步實現了。github
簡單版Promise
1. promise是一個類,它的構造函數接受一個函數,函數的兩個參數也都是函數segmentfault
第一點比較簡單數組
// 這裏沒有使用Promise做爲類名是爲了方便測試
class WPromise {
constructor(executor) {
// 這裏綁定this是爲了防止執行時this的指向改變,this的指向問題,這裏不過多贅述
executor(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
}
_resolve() {}
_reject() {}
}
2. 在傳入的函數中執行resolve表示成功,執行reject表示失敗,傳入的值會傳給then方法的回調函數promise
成功、失敗,這個很容易想到使用一個狀態進行標記,實際上Promise就是這樣作的。在Promise中使用了pending、fulfilled、rejected來標識當前的狀態。異步
-
pending初始狀態,既不是成功,也不是失敗狀態。等待resolve或者reject調用更新狀態。 -
fulfilled意味着操做成功完成。 -
rejected意味着操做失敗。
須要注意的一點是,這三個狀態之間只存在兩個變換關係:函數
-
pending轉換爲fulfilled,只能由resolve方法完成轉換 -
pending轉換爲rejected,只能由reject方法完成轉換
傳入的值會傳給then的回調函數,怎麼傳遞呢?顯然咱們將對resolve和reject的值作一個保存。
將上面的狀態和值添加到Promise
class WPromise {
static pending = 'pending';
static fulfilled = 'fulfilled';
static rejected = 'rejected';
constructor(executor) {
executor(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
this.status = WPromise.pending; // 初始化狀態爲pending
this.value = undefined; // 存儲 this._resolve 即操做成功 返回的值
this.reason = undefined; // 存儲 this._reject 即操做失敗 返回的值
}
_resolve(value) {
this.value = value;
this.status = WPromise.fulfilled; // 將狀態設置爲成功
}
_reject(reason) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = WPromise.rejected; // 將狀態設置爲失敗
}
}
3. Promise有一個叫作then的方法,該方法有兩個參數,第一個參數是成功以後執行的回調函數,第二個參數是失敗以後執行的回調函數。then方法在resolve或者reject執行以後纔會執行,而且then方法中的值是傳給resolve或reject的參數
這句話有點長,須要注意的是這句then方法在resolve或者reject執行以後纔會執行,咱們知道Promise是異步的,也就是說then傳入的函數是不能立馬執行,須要存儲起來,在resolve函數執行以後纔拿出來執行。
換句話說,這個過程有點相似於發佈訂閱者模式:咱們使用then來註冊事件,那何時來通知這些事件是否執行呢?答案就是在resolve方法執行或者reject方法執行時。
ok, 繼續完善咱們的代碼。
class WPromise {
static pending = "pending";
static fulfilled = "fulfilled";
static rejected = "rejected";
constructor(executor) {
executor(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
this.status = WPromise.pending; // 初始化狀態爲pending
this.value = undefined; // 存儲 this._resolve 即操做成功 返回的值
this.reason = undefined; // 存儲 this._reject 即操做失敗 返回的值
// 存儲then中傳入的參數
// 至於爲何是數組呢?由於同一個Promise的then方法能夠調用屢次
this.callbacks = [];
}
// onFulfilled 是成功時執行的函數
// onRejected 是失敗時執行的函數
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 這裏能夠理解爲在註冊事件
// 也就是將須要執行的回調函數存儲起來
this.callbacks.push({
onFulfilled,
onRejected,
});
}
_resolve(value) {
this.value = value;
this.status = WPromise.fulfilled; // 將狀態設置爲成功
// 通知事件執行
this.callbacks.forEach((cb) => this._handler(cb));
}
_reject(reason) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = WPromise.rejected; // 將狀態設置爲失敗
this.callbacks.forEach((cb) => this._handler(cb));
}
_handler(callback) {
const { onFulfilled, onRejected } = callback;
if (this.status === WPromise.fulfilled && onFulfilled) {
// 傳入存儲的值
onFulfilled(this.value);
}
if (this.status === WPromise.rejected && onRejected) {
// 傳入存儲的錯誤信息
onRejected(this.reason);
}
}
}
這個時候的Promise已經漸具雛形,如今能夠來簡單測試一下
function fetchData(success) {
return new WPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (success) {
resolve("willem");
} else {
reject('error');
}
}, 1000);
});
}
fetchData(true).then(data => {
console.log(data); // after 1000ms: willem
});
fetchData(false).then(null, (reason) => {
console.log(reason); // after 1000ms: error
});
從上面的輸出結果來看,暫時是沒什麼問題的。接下來就是須要重點關注的鏈式調用問題了。
重難點:鏈式調用
鏈式調用 不知道大家看見這個想到了啥,我反正是想到了jQuery。其實鏈式調用無非就是再返回一個類的實例,那首先想到的確定就是直接返回this,不過反正自身真的能夠嗎?
咱們不妨在then方法最後添加一行 return this;來進行一個測試
function fetchData() {
return new WPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('willem');
}, 1000);
});
}
const p1 = fetchData().then(data1 => {return data1 + ' wei'});
const p2 = p1.then((data2) => {console.log(data2);}); // willem 正確輸出應該是 'willem wei'
const p3 = p1.then((data3) => {console.log(data3);}); // willem 正確輸出應該是 'willem wei'
顯然,直接返回this是確定不對,確定要對函數的返回值作一個處理。
這時候可能會有同窗說了,那我處理不就完事了麼,我把then回調函數的執行結果賦值給value不就完事。答案固然是否認的,這回引起Promise內部的value和callbacks混亂。
那麼,咱們採起的固然是另外一個方案,每次then方法都將返回一個新的Promise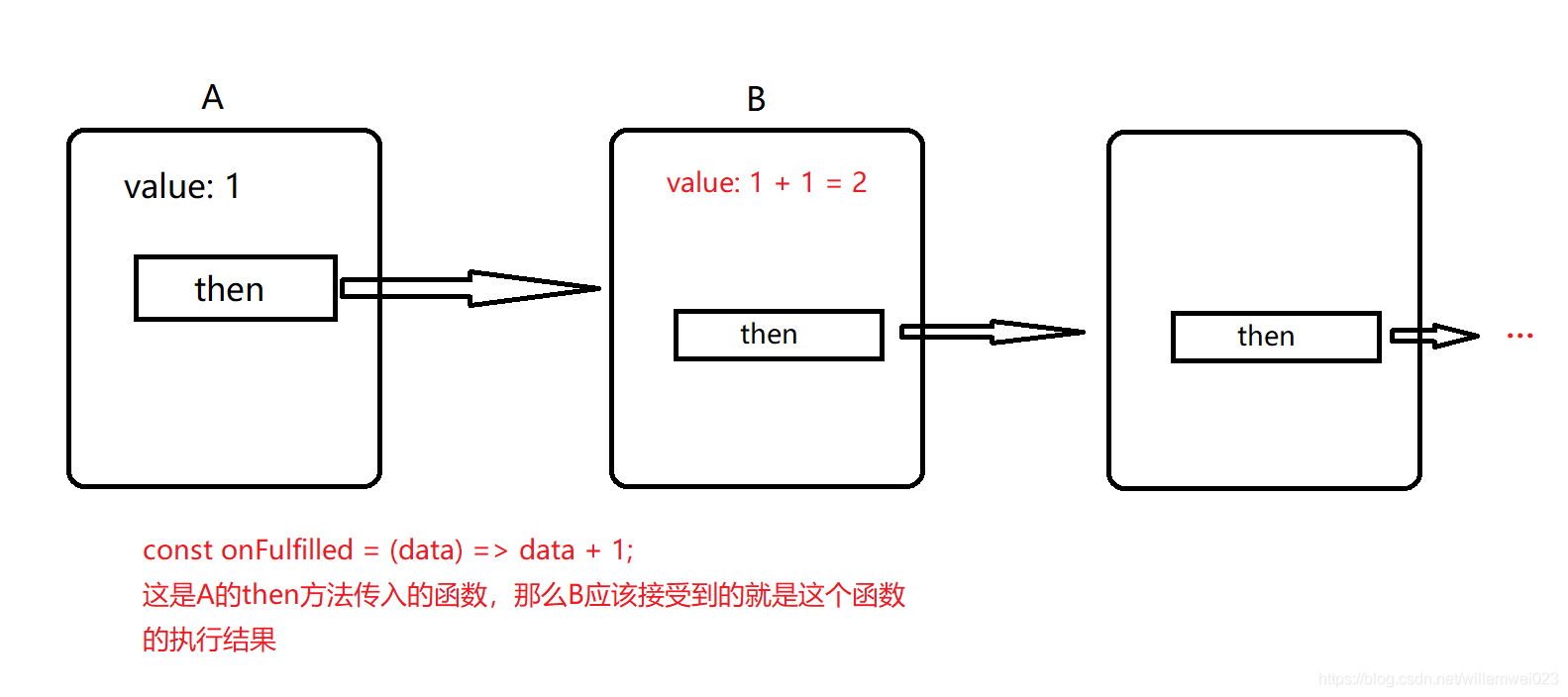
這是一個簡單的then的數據走向。簡單說一下,then函數中返回的Promise的value值來源於當前then函數的onFulfilled函數(第一個參數)的執行結果(爲方便理解,暫時只討論操做成功的狀況)。
從咱們寫的代碼來看,value值只會在resolve函數中被賦值,顯然咱們也將會把onFulfilled執行的結果經過resolve的執行來傳入到下一個Promise中。
加入鏈式調用的處理:
class WPromise {
static pending = "pending";
static fulfilled = "fulfilled";
static rejected = "rejected";
constructor(executor) {
executor(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
this.status = WPromise.pending; // 初始化狀態爲pending
this.value = undefined; // 存儲 this._resolve 即操做成功 返回的值
this.reason = undefined; // 存儲 this._reject 即操做失敗 返回的值
// 存儲then中傳入的參數
// 至於爲何是數組呢?由於同一個Promise的then方法能夠調用屢次
this.callbacks = [];
}
// onFulfilled 是成功時執行的函數
// onRejected 是失敗時執行的函數
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 返回一個新的Promise
return new WPromise((nextResolve, nextReject) => {
// 這裏之因此把下一個Promsie的resolve函數和reject函數也存在callback中
// 是爲了將onFulfilled的執行結果經過nextResolve傳入到下一個Promise做爲它的value值
this.callbacks.push({
nextResolve,
nextReject,
onFulfilled,
onRejected
});
});
}
_resolve(value) {
this.value = value;
this.status = WPromise.fulfilled; // 將狀態設置爲成功
// 通知事件執行
this.callbacks.forEach((cb) => this._handler(cb));
}
_reject(reason) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = WPromise.rejected; // 將狀態設置爲失敗
this.callbacks.forEach((cb) => this._handler(cb));
}
_handler(callback) {
const { onFulfilled, onRejected, nextResolve, nextReject } = callback;
if (this.status === WPromise.fulfilled) {
// 傳入存儲的值
// 未傳入onFulfilled時,將undefined傳入
const nextValue = onFulfilled ? onFulfilled(this.value) : undefined;
nextResolve(nextValue);
return;
}
if (this.status === WPromise.rejected) {
// 傳入存儲的錯誤信息
// 一樣的處理
const nextReason = onRejected ? onRejected(this.value) : undefined;
nextReject(nextReason);
}
}
}
咱們再把剛開始的例子拿來測試一下
function fetchData() {
return new WPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('willem');
}, 1000);
});
}
fetchData().then((data) => {
// after 1000ms
console.log(data); // willem
return 'wei';
}, (err) => {}).then((data2) => {
console.log(data2); // wei
});
喲西,沒啥問題。不過上面的版本還有個問題沒有處理,當onFulfilled執行的結果不是一個簡單的值,而就是一個Promise時,後續的then會等待其執行完成以後才執行。
Promise基礎版的最終版:
class WPromise {
static pending = "pending";
static fulfilled = "fulfilled";
static rejected = "rejected";
constructor(executor) {
executor(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
this.status = WPromise.pending; // 初始化狀態爲pending
this.value = undefined; // 存儲 this._resolve 即操做成功 返回的值
this.reason = undefined; // 存儲 this._reject 即操做失敗 返回的值
// 存儲then中傳入的參數
// 至於爲何是數組呢?由於同一個Promise的then方法能夠調用屢次
this.callbacks = [];
}
// onFulfilled 是成功時執行的函數
// onRejected 是失敗時執行的函數
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 返回一個新的Promise
return new WPromise((nextResolve, nextReject) => {
// 這裏之因此把下一個Promsie的resolve函數和reject函數也存在callback中
// 是爲了將onFulfilled的執行結果經過nextResolve傳入到下一個Promise做爲它的value值
this.callbacks.push({
nextResolve,
nextReject,
onFulfilled,
onRejected
});
});
}
_resolve(value) {
// 處理onFulfilled執行結果是一個Promise時的狀況
// 這裏可能理解起來有點困難
// 當value instanof WPromise時,說明當前Promise確定不會是第一個Promise
// 而是後續then方法返回的Promise(第二個Promise)
// 咱們要獲取的是value中的value值(有點繞,value是個promise時,那麼內部存有個value的變量)
// 怎樣將value的value值獲取到呢,能夠將傳遞一個函數做爲value.then的onFulfilled參數
// 那麼在value的內部則會執行這個函數,咱們只須要將當前Promise的value值賦值爲value的value便可
if (value instanceof WPromise) {
value.then(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
return;
}
this.value = value;
this.status = WPromise.fulfilled; // 將狀態設置爲成功
// 通知事件執行
this.callbacks.forEach((cb) => this._handler(cb));
}
_reject(reason) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = WPromise.rejected; // 將狀態設置爲失敗
this.callbacks.forEach((cb) => this._handler(cb));
}
_handler(callback) {
const { onFulfilled, onRejected, nextResolve, nextReject } = callback;
if (this.status === WPromise.fulfilled) {
// 傳入存儲的值
// 未傳入onFulfilled時,將undefined傳入
const nextValue = onFulfilled ? onFulfilled(this.value) : undefined;
nextResolve(nextValue);
return;
}
if (this.status === WPromise.rejected) {
// 傳入存儲的錯誤信息
// 一樣的處理
const nextReason = onRejected ? onRejected(this.value) : undefined;
nextReject(nextReason);
}
}
}
ok,測試一下
function fetchData() {
return new WPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('willem');
}, 1000);
});
}
fetchData().then((data) => {
return new WPromise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(data + ' wei');
}, 1000);
});
}, (err) => {}).then((data2) => {
console.log(data2); // willem wei
});
至此,一個簡單的Promise就完成了,固然還有不少須要處理,好比異常等等。
下一篇文章咱們一塊兒再來學習一下finally和catch的實現。
- 1. 【原】手寫一個promise 手把手教你實現一個完整的 Promise
- 2. 手寫一個Promise
- 3. 手寫一個promise
- 4. 手寫實現promise
- 5. 手寫實現Promise
- 6. 學習Promise基礎及手寫Promise
- 7. 請手寫代碼實現一個promise
- 8. Promise-手寫Promise
- 9. 手寫基於Promise A+規範的Promise
- 10. es6 --- > 手寫一個promise
- 更多相關文章...
- • 現實生活中的 XML - XML 教程
- • Scala 基礎語法 - Scala教程
- • ☆基於Java Instrument的Agent實現
- • Kotlin學習(一)基本語法
-
每一个你不满意的现在,都有一个你没有努力的曾经。