Spring源碼分析之IOC的三種常見用法及源碼實現(一)
1.ioc核心功能bean的配置與獲取api
有如下四種java

(來自精通spring4.x的p175)spring
經常使用的是前三種api
第一種方式
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 指定class屬性,經過構造方法建立Bean實例 -->
<bean id="person" class="com.mao.gouzao.Person">
</bean>
</beans>
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
System.out.println(ctx.getBean("person"));
}
第二種方式
定義緩存
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl {
public void test(){
System.out.println(666);
}
}
獲取app
@Autowired private static UserServiceImpl userService;
第三種方式
定義ide
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
@Bean
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}
注意: 經過@Bean的形式是使用的話,bean的默認名稱是方法名,若Bean(value="bean"的名稱")那麼bean的名稱是指定的源碼分析
去容器中讀取Bean的信息(傳入配置類) ui
獲取this
public static void main( String[] args )
{
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
System.out.println(ctx.getBean("person"));
}
2.如何實現的
1.基於Java類配置的實現方式源碼分析
1.就執行了這兩句代碼lua
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
System.out.println(ctx.getBean("person"));
先看看,打開構造器源碼:
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
this();
register(annotatedClasses);
refresh();
}
2.首先不急,主角兒AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 它有父類,由於類初始化順序的關係,會先初始化父類,因此得看父類,一直看到最後父類爲DefaultResourceLoader
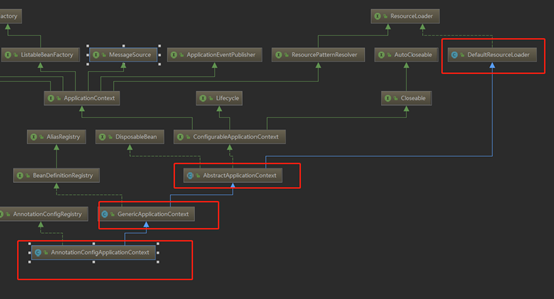
DefaultResourceLoader,很明顯是用來加載資源的,倒數第二個AbstractApplicationContext的無參構造中也是初始化一個加載資源相關:
Ok,再來看最後一個父類GenericApplicationContext了,父類默認初始化使用下面這個無參的
public GenericApplicationContext() {
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}
這裏是建立了springioc體系中的一個重要的類DefaultListableBeanFactory,DefaultListableBeanFactory很是關鍵裏面實現了ioc相關不少功能,能夠提供給咱們的AnnotationConfigApplicationContext使用(後面會看到)
3.ok父類都看完了,那就回到咱們的主角兒AnnotationConfigApplicationContext了
咱們來看它的構造器剛剛是什麼代碼(迴歸自己):
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
就兩行。
4.先看第一句this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
進去
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this(registry, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry));
}
它再次調用本身的構造器
這裏還涉及了一個方法getOrCreateEnvironment(registry)
很明顯這個方法從名字看就知道是有緩存的意思,獲取或建立,若是是第一次則建立 第二次則就是獲取了,第二次拿的第一次緩存的。以下:
private static Environment getOrCreateEnvironment(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
if (registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
return ((EnvironmentCapable) registry).getEnvironment();
}
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
ok,繼續看,剛剛是從構造器到另外一個構造器了:
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
ConditionEvaluator是計算conditon的解析器(後面會講),這裏很明顯主要邏輯在 AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
接下來AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);是重中之重,終於開始有大段邏輯了!以前都是各類繼承跳轉!
registerAnnotationConfigProcessors源碼實現以下
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>(4);
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
}
挺長,先看第一部分:
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
很明顯這是從registry裏拿DefaultListableBeanFactory ,還記得前面講主角兒AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的父類GenericApplicationContext嗎?在它的無參構造中就建立了DefaultListableBeanFactory。如今到這個registry裏去拿,而這個registry就是前面用this傳過來的主角兒AnnotationConfigApplicationContext天然就有DefaultListableBeanFactory了。後面的邏輯就是null判斷和設置比較器和解析器到裏面了。
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>(4);
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
建立了一個set集合保存BeanDefinitionHolder(BeanDefinition是)。後面就很是多的if判斷。這都是判斷啥呢?
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
判斷registry中是否存在一個個的常量定義的東西。那這些常量是什麼呢?打開一看:
public static final String CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME = "org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor";
是個類的全路徑,若是registry裏面沒有就執行最後一句(前兩句都是給最後一句服務的):
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
也就是判斷有沒有這個類,沒有就添加這個類進去,這這個類是用來解析配置註解的處理器。
還有個 public static final String AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME = "org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor";
綜合所見,這段代碼後半部分其實就是註冊spring支持的各類註解的解析器的邏輯
這個對應是用來解析自動裝配註解的
最後以下:
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
//獲取以前建立的DefaultListableBeanFactory,檢查null並塞入相關組件
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>(8);
//註冊一個配置類@Configuration解析器的bean定義(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//設置AutoWired註解解析器的bean定義信息
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//註冊解析@Required 註解的處理器
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//檢查是否支持JSR250規範,如何支持註冊 解析JSR250規範的註解
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//檢查是否支持jpa,若支持註冊解析jpa規範的註解
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//註冊解析@EventListener的註解解析器
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
//最後帶着這一堆spring支持的功能的解析器返回(實際上剛剛分析的過程當中壓根沒用到這個返回值,那是爲何呢?值得注意的是 原來它是把這些搞到registry裏去了,綜上, 注入這堆註解解析器 到registry 也就是DefaultListableBeanFactory中!)
return beanDefs;
}
好,以上這部分分析結束,回到主角兒AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,以前咱們是從它的構造器:
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
中分析的第一句終於把這個reader完畢了,接下來分析第二句咯。
名字能夠看出是類路徑下的掃描器,開始查看源碼!
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this(registry, true);
}
繼續跟進
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean useDefaultFilters) {
this(registry, useDefaultFilters, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry));
}
第一個registry 仍是以前說的DefaultListableBeanFactory傳的this,第二個也就是 傳了個true,是否使用默認的filter,選擇了是。第三個以前講過了,有則用沒有則建立,緩存。繼續跟
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean useDefaultFilters,
Environment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
if (useDefaultFilters) {
registerDefaultFilters();
}
setEnvironment(environment);
setResourceLoader(resourceLoader);
}
這部分代碼前面就是賦值、註冊默認的filters、設置從registry拿的環境設置、最後設置ResourceLoader
一部分一部分的看,先看registerDefaultFilters();
/**
* Register the default filter for {@link Component @Component}.
* <p>This will implicitly register all annotations that have the
* {@link Component @Component} meta-annotation including the
* {@link Repository @Repository}, {@link Service @Service}, and
* {@link Controller @Controller} stereotype annotations.
* <p>Also supports Java EE 6's {@link javax.annotation.ManagedBean} and
* JSR-330's {@link javax.inject.Named} annotations, if available.
*
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void registerDefaultFilters() {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class));
ClassLoader cl = ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.class.getClassLoader();
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.annotation.ManagedBean", cl)), false));
logger.debug("JSR-250 'javax.annotation.ManagedBean' found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-250 1.1 API (as included in Java EE 6) not available - simply skip.
}
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Named", cl)), false));
logger.debug("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Named' annotation found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}
方法註釋能夠看到 意思是,註冊這些默認的filter,@Component、@Repository、@Controller纔會起做用
而後方法內部就注入添加Component.class進去了,讓@Component起做用,而@Repository、@Controller自己都被打了@Component 是子註解,因此也連帶起做用
後面部分就是判斷jsr250 330相關注解了
到此看完了,回到上層上層去,至此
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super(beanFactory);
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
中的第二句咱們也大體看完了,至此一個構造器看完了。大功告成.......了,一半。。。發現這個構造器是無參的,而咱們以前用的兩句代碼:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplication = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext (MainConfig.class);Person person2 = (Person)annotationConfigApplication.getBean("person2");
中主角AnnotationConfigApplicationContext用的帶class的構造器啊,看來沒完,原來這個構造器還有上層調用,在這:
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
this();
register(annotatedClasses);
refresh();
}
這裏纔是最開始那兩行代碼的第一次調用處。咱們把this();看完了!
接下來看第二句register(annotatedClasses);,不斷跟進
public void register(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
Assert.notEmpty(annotatedClasses, "At least one annotated class must be specified");
this.reader.register(annotatedClasses);
}
不斷跟進到這
public void registerBean(Class<?> annotatedClass, String name, Class<? extends Annotation>... qualifiers) {
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(annotatedClass);
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
}
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
if (qualifiers != null) {
for (Class<? extends Annotation> qualifier : qualifiers) {
if (Primary.class == qualifier) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) {
abd.setLazyInit(true);
}
else {
abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier));
}
}
}
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
原來這句代碼是把傳入的配置類裏的bean全給註冊了。至此第二句完畢。至於最後第三句核心,留給下篇文章。一塊兒加油!
- 1. Spring源碼分析之IOC的三種常見用法及源碼實現(一)
- 2. Spring源碼分析之IOC的三種常見用法及源碼實現(三)
- 3. Spring源碼分析之IOC的三種常見用法及源碼實現(二)
- 4. Spring IOC源碼分析(一)
- 5. Spring 源碼分析(二)之 Spring IOC 容器源碼分析
- 6. Spring IOC源碼分析三:Spring refresh下
- 7. spring IOC源碼分析(1)
- 8. Spring IoC 源碼分析
- 9. Spring ioc源碼分析
- 10. Spring IOC 源碼分析
- 更多相關文章...
- • Spring實例化Bean的三種方法 - Spring教程
- • Spring Bean的配置及常用屬性 - Spring教程
- • 互聯網組織的未來:剖析GitHub員工的任性之源
- • Java Agent入門實戰(二)-Instrumentation源碼概述
-
每一个你不满意的现在,都有一个你没有努力的曾经。