nodejs負載均衡(一):服務負載均衡
什麼是負載均衡
負載平衡(Load balancing)是一種 計算機技術,用來在多個計算機( 計算機集羣)、網絡鏈接、CPU、磁盤驅動器或其餘資源中分配負載,以達到最優化資源使用、最大化吞吐率、最小化響應時間、同時避免過載的目的。 使用帶有負載平衡的多個服務器組件,取代單一的組件,能夠經過 冗餘提升可靠性。負載平衡服務一般是由專用軟件和硬件來完成。 主要做用是將大量做業合理地分攤到多個操做單元上進行執行,用於解決互聯網架構中的 高併發和 高可用的問題。 - wiki
負載均衡(Load Balance)是創建在網絡協議分層上的,經過網絡協議裏面的處理將負載的做業合理的分攤到多個操做單元上。javascript

因此針對網絡協議層有不一樣負載均衡策略 2/3/4/7層負載均衡 ,負載均衡的實現分 軟/硬,顧名思義:java
- 一個是經過軟件實現,成本低、靈活簡單,缺點受服務器性能影響
- 一個是經過硬件,性能優於軟負載均衡,可是成本高
nodejs能作哪些
先看下面的請求鏈路圖(舉個例子,實現方式、策略、架構等有不少)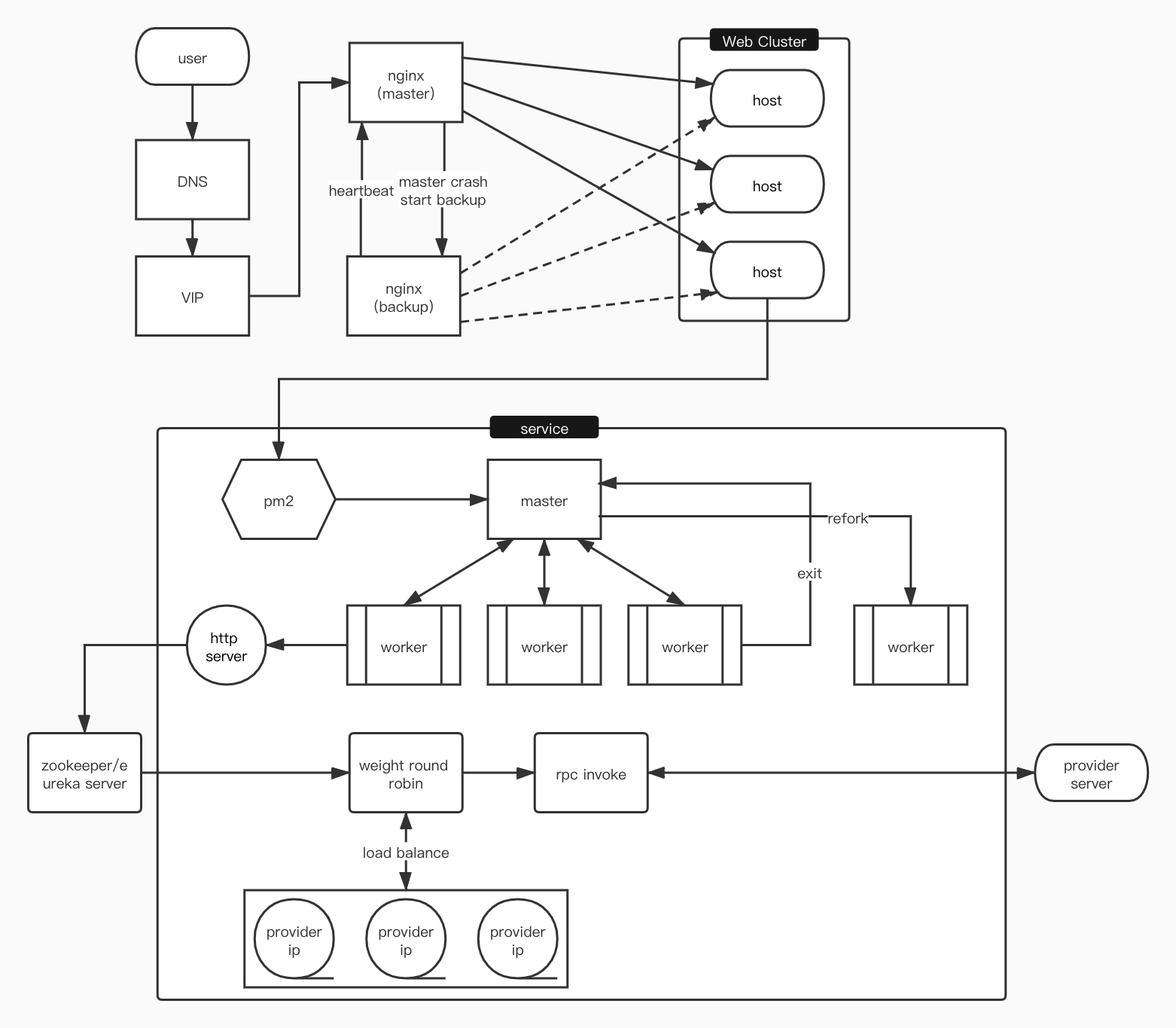 node
node
- DNS、VIP、Nginx服務的負載均衡底層服務(雲)或者運維已經搭建好了,不需node開發過多關心
- Nginx負載均衡到web服務集羣,可使用
upstream模塊配置不一樣策略 - 重點node單個服務負載均衡,主進程分派到多個子進程,這是屬於軟負載均衡
- 假如node服務要經過RPC調用遠程其餘服務,爲了避免影響其餘服務,須要將RPC均衡分派到其餘服務的不一樣節點上
結論:從上面看出三、4是nodejs服務能夠作的,就是 服務負載均衡 和 rpc負載均衡git
服務負載均衡
先了解一下nodejs cluster模塊,下面是nodejs官方cluster例子代碼github
app.js web
const cluster = require('cluster');
const http = require('http');
const numCPUs = require('os').cpus().length;
if (cluster.isMaster) {
console.log(`Master ${process.pid} is running`);
// Fork workers.
for (let i = 0; i < numCPUs; i++) {
cluster.fork();
}
cluster.on('exit', (worker, code, signal) => {
console.log(`worker ${worker.process.pid} died`);
});
} else {
// Workers can share any TCP connection
// In this case it is an HTTP server
http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200);
res.end('hello world\n');
}).listen(8000);
console.log(`Worker ${process.pid} started`);
}
- 啓動
app.js,當前執行進程是主線程 - 而後會
fork與cpu個數同樣的worker進程 - worker進程默認執行
process.argv[1]文件,即app.js - 當非
master進程程啓動http server,每一個worker進程啓動一個
1.如何監聽同一個端口
第一個問題:爲何多個進程server能夠監聽同一個port?算法
The first one (and the default one on all platforms except Windows), is the round-robin approach, where the master process listens on a port, accepts new connections and distributes them across the workers in a round-robin fashion, with some built-in smarts to avoid overloading a worker process.
第一種方法(也是除 Windows 外全部平臺的默認方法)是循環法,由主進程負責監聽端口,接收新鏈接後再將鏈接循環分發給工做進程,在分發中使用了一些內置技巧防止工做進程任務過載。The second approach is where the master process creates the listen socket and sends it to interested workers. The workers then accept incoming connections directly.
第二種方法是,主進程建立監聽 socket 後發送給感興趣的工做進程,由工做進程負責直接接收鏈接。dockerThe second approach should, in theory, give the best performance. In practice however, distribution tends to be very unbalanced due to operating system scheduler vagaries. Loads have been observed where over 70% of all connections ended up in just two processes, out of a total of eight.
理論上第二種方法應該是效率最佳的。 但在實際狀況下,因爲操做系統調度機制的難以捉摸,會使分發變得不穩定。 可能會出現八個進程中有兩個分擔了 70% 的負載。shell
官方支持2種方法,其實都是主進程負責監聽端口,子進程會fork一個handle句柄給主線,經過循環分發或監聽發送與worker進程通訊,交替處理任務。json
2.進程間如何通訊
第二個問題:進程間如何通訊?
一、主進程和子進程
主進程和子進程經過 IPC 通訊
app.js
const cluster = require('cluster');
const http = require('http');
const numCPUs = require('os').cpus().length;
if (cluster.isMaster) {
console.log(`Master ${process.pid} is running`);
// Fork workers.
for (let i = 0; i < numCPUs; i++) {
cluster.fork();
}
cluster.on('exit', (worker, code, signal) => {
console.log(`worker ${worker.process.pid} died`);
});
cluster.on('listening', (worker) => {
// send to worker
worker.send({message: 'from master'})
});
for (const id in cluster.workers) {
cluster.workers[id].on('message', (data)=>{
// receive by the worker
console.log('master message: ', data)
});
}
} else {
// Workers can share any TCP connection
// In this case it is an HTTP server
http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200);
res.end('hello world\n');
}).listen(8000);
console.log(`Worker ${process.pid} started`);
// send to master
process.send({message: 'from worker'})
process.on('message', (data)=>{
// receive by the master
console.log('worker message', data)
})
}
這是經過node的原生ipc通訊,ipc通訊方式有不少種
- node原先ipc channel
- shell stdin/stdout
- socket
- pipe
- message queues
二、子進程與子進程
- 一對多,能夠經過父進程進行分發
- 一對一,能夠經過ipc通訊
3.如何作到進程負載均衡
第三個問題:如何作到進程負載均衡?
服務器集羣的負載均衡經過上層已經處理了(Nginx、DNS、VIP等),那node服務怎麼作的?cluster採用 round-robin 算法策略分發http請求到不一樣worker進程,關於負載均衡算法下一章《nodejs負載均衡(二):RPC負載均衡》裏面會講
4.服務異常退出怎麼辦
第四個問題:服務異常退出怎麼辦?
- 通常能夠經過
try/catch捕獲異常錯誤,可是node裏面若是遺漏異常捕獲,可能致使整個進程崩潰 - 使用
try/catch就夠了嗎?異常會冒泡到event loop,觸發uncaughtException事件,這裏能夠阻止程序退出 - node異常默認狀況是打印
stderr並以代碼1退出,觸發exit事件 - 當異常退出時,主線程監聽到worker死亡,能夠refork一個新的worker
Tips: 退出的事件還有
Signal Events
如今來看下 graceful.js 大概實現,在下一節會有完整的代碼,完整案例查看graceful-shutdown-example
'use strict';
module.exports = options => {
const { processKillTimeout = 3000, server } = options;
let throwErrorTimes = 0
process.on('uncaughtException', function(err) {
throwErrorTimes += 1;
console.log('====uncaughtException====');
console.error(err)
if (throwErrorTimes > 1) {
return;
}
close()
});
function close(){
server.close(() => {
// ...do something
})
}
};
5.如何平滑退出
第五個問題:如何平滑退出?
在發佈時,多臺機器分組發佈,能夠保證服務不會不可訪問,可是:
- 用戶正在訪問一臺下線的服務,如何確保等待用戶請求返回在下線?
- 一個worker服務異常退出,如何平滑重啓一個worker?
一個平滑退出的大概流程:
- fork worker
- 監聽worker狀態
- worker異常退出refork
- 監聽master signal退出信號
- master退出前kill全部worker
- worker退出前close server和worker的子進程
// master.js
'use strict';
const cluster = require('cluster');
const killTree = require('./kill-tree');
const numCPUs = require('os').cpus().length;
// const numCPUs = 1;
let stopping = false;
console.log(`Master ${process.pid} is running`);
cluster.setupMaster({
exec: 'worker.js',
// silent: true,
});
// Fork workers.
for (let i = 0; i < numCPUs; i++) {
cluster.fork();
}
cluster.on('fork', worker => {
worker.on('message', data => {
// Receive by the worker
console.log(`${worker.process.pid} master message: `, data);
});
});
// Kill all workers
async function onMasterSignal() {
if (stopping) return;
stopping = true;
const killsCall = Object.keys(cluster.workers).map(id => {
const worker = cluster.workers[id];
return killTree(worker.process.pid);
});
await Promise.all(killsCall);
}
// kill(2) Ctrl-C
// kill(3) Ctrl-\
// kill(15) default
// Master exit
['SIGINT', 'SIGQUIT', 'SIGTERM'].forEach(signal => {
process.once(signal, onMasterSignal);
});
// Terminate the master process
process.once('exit', () => {
console.log(`Master about to exit`);
});
// Worker is listening
cluster.on('listening', (worker, address) => {
// Send to worker
worker.send({ message: 'from master' });
});
cluster.on('disconnect', worker => {
console.log(`${worker.id} disconnect`);
});
// Worker died
cluster.on('exit', (worker, code, signal) => {
console.log(
`Worker ${worker.process.pid} died, code: ${code}, signal: ${signal}`
);
worker.removeAllListeners();
// killTree(worker.process.pid, function(err) {
// console.log(err)
// });
// stopping server
if (stopping) return;
console.log('====Refork====');
// refork a new worker
cluster.fork();
});
setTimeout(() => {
cluster.workers[1].send({
action: 'throw error',
});
}, 600);
// worker.js
'use strict';
const http = require('http');
const { fork } = require('child_process');
const graceful = require('./graceful');
fork('./child');
// Workers can share any TCP connection
// In this case it is an HTTP server
const server = http
.createServer((req, res) => {
// services excption
try {
throw new Error('Happened error');
} catch (err) {
res.writeHead(200);
res.end(`${err.stack.toString()}`);
}
// console.log(res)
// res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json');
// res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
// res.writeHead(200);
// res.end(JSON.stringify({ success: true }));
})
.listen(8000);
graceful({
server,
});
// Send to master
process.send({
message: 'from worker',
// server
});
process.on('message', data => {
// Receive by the master
if (data.action && data.action === 'throw error') {
// The process threw an exception
throw new Error('Kill myself');
}
console.log('Worker message', data);
});
**
// graceful.js
'use strict';
const cluster = require('cluster');
const killTree = require('./kill-tree');
module.exports = options => {
const { processKillTimeout = 3000, server } = options;
let throwErrorTimes = 0
process.on('SIGTERM', function onSigterm () {
console.info(`Only graceful shutdown, worker ${process.pid}`)
close()
})
process.on('uncaughtException', function(err) {
throwErrorTimes += 1;
console.log('====uncaughtException====');
console.error(err)
if (throwErrorTimes > 1) {
return;
}
close()
});
function close(){
server.on('request', (req, res) => {
// closing the http request
req.shouldKeepAlive = false;
res.shouldKeepAlive = false;
if (!res._header) {
// closing the socket connection
res.setHeader('Connection', 'close');
}
});
if (processKillTimeout) {
const timer = setTimeout(() => {
// Kill all child process
killTree(process.pid,()=>{
// Worker process to exit
process.exit(1);
})
}, processKillTimeout);
timer.unref && timer.unref();
}
const worker = cluster.worker;
if (worker) {
try {
server.close(() => {
try {
worker.send({ message: 'disconnect' });
worker.disconnect();
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error on worker disconnect');
}
});
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error on server close');
}
}
}
};
完整案例查看graceful-shutdown-example
6.守護進程或主進程掛了怎麼辦
第六個問題: 守護進程或主進程掛了怎麼辦?
防止出現單點故障,提供主從備份服務器。
7.主動中止服務
- 經過系統命令獲取當前node進程信息
- 過濾中止腳本進程,獲取啓動腳本進程
- kill master進程,發送
SIGTERM - 主進程監聽到
SIGTERM,開始kill workers,中止server
// stop.js
const main = async () => {
const command = isWin
? 'wmic Path win32_process Where "Name = \'node.exe\'" Get CommandLine,ProcessId'
: // command, cmd are alias of args, not POSIX standard, so we use args
'ps -eo "pid,args" | grep node';
}
// ...
main().then((result)=>{
result.forEach((item)=>{
process.kill(item.pid, 'SIGTERM')
// killTree(item.pid)
});
})
// master.js
// kill(2) Ctrl-C
// kill(3) Ctrl-\
// kill(15) default
// Master exit
['SIGINT', 'SIGQUIT', 'SIGTERM'].forEach(signal => {
process.once(signal, onMasterSignal);
});
完整案例查看graceful-shutdown-example,真正要實現一個合理node負載均衡框架,還須要作好 worker 管理及 IPC 通訊機制、不一樣系統兼容性、docker、sticky模式等等
下一章節再聊下 《nodejs負載均衡(二):RPC負載均衡》 的實現。
- 1. Ribbon(負載均衡)負載均衡
- 2. 客戶端負載均衡與服務端負載均衡
- 3. 客戶端負載均衡,服務端口負載均衡
- 4. 服務器負載均衡和客戶端負載均衡
- 5. 服務器負載均衡
- 6. 負載均衡(一)
- 7. Nginx 負載均衡 NodeJS~
- 8. 負載均衡
- 更多相關文章...
- • ionic 加載動作 - ionic 教程
- • ionic 加載動畫 - ionic 教程
- • Spring Cloud 微服務實戰(三) - 服務註冊與發現
- • RxJava操作符(一)Creating Observables
-
每一个你不满意的现在,都有一个你没有努力的曾经。
- 1. eclipse設置粘貼字符串自動轉義
- 2. android客戶端學習-啓動模擬器異常Emulator: failed to initialize HAX: Invalid argument
- 3. android.view.InflateException: class com.jpardogo.listbuddies.lib.views.ListBuddiesLayout問題
- 4. MYSQL8.0數據庫恢復 MYSQL8.0ibd數據恢復 MYSQL8.0恢復數據庫
- 5. 你本是一個肉體,是什麼驅使你前行【1】
- 6. 2018.04.30
- 7. 2018.04.30
- 8. 你本是一個肉體,是什麼驅使你前行【3】
- 9. 你本是一個肉體,是什麼驅使你前行【2】
- 10. 【資訊】LocalBitcoins達到每週交易比特幣的7年低點
- 1. Ribbon(負載均衡)負載均衡
- 2. 客戶端負載均衡與服務端負載均衡
- 3. 客戶端負載均衡,服務端口負載均衡
- 4. 服務器負載均衡和客戶端負載均衡
- 5. 服務器負載均衡
- 6. 負載均衡(一)
- 7. Nginx 負載均衡 NodeJS~
- 8. 負載均衡