Nacos 1.3.0-BETA 即未來襲,此次來波大的!
本文來自於個人公衆號 程序猿天璇:Nacos 1.3.0-BETA 即未來襲,此次來波大的!,轉載請保留連接 ;)java
概述
本次1.3.0-BETA的改動程度很大,涉及兩個模塊的修改以及新增一個核心模塊。node
- nacos-core模塊修改
a. nacos集羣節點成員尋址模式的統一管理
b. nacos內部事件機制
c. nacos一致性協議層 - nacos-config模塊修改
a. 新增內嵌分佈式數據存儲組件
b. 內嵌存儲與外置存儲細分
c. 內嵌存儲簡單運維 - nacos-consistency模塊新增
a. 對於AP協議以及CP協議的統一抽象
Nacos的將來總體邏輯架構及其組件

Nacos集羣成員節點尋址模式
在1.3.0-BETA以前,nacos的naming模塊以及config模塊存在各自的集羣成員節點列表管理任務。爲了統一nacos集羣下成員列表的尋址模式,將集羣節點管理的實現從naming模塊以及config模塊剝離出來,統一下沉到了core模塊的尋址模式,同時新增命令參數-Dnacos.member.list進行設置nacos集羣節點列表,該參數能夠看做是cluster.conf 文件的一個替代。 前nacos的尋址模式類別以下:mysql
- a. 單機模式:StandaloneMemberLookup
-
b. 集羣模式:git
- i.cluster.conf 件存在:FileConfigMemberLookup
- ii.nacos.member.discovery==true:DiscoveryMemberLookup
- iii.cluster.conf 件不存在或者 -Dnacos.member.list沒有設置:
AddressServerMemberLookupgithub
邏輯圖以下: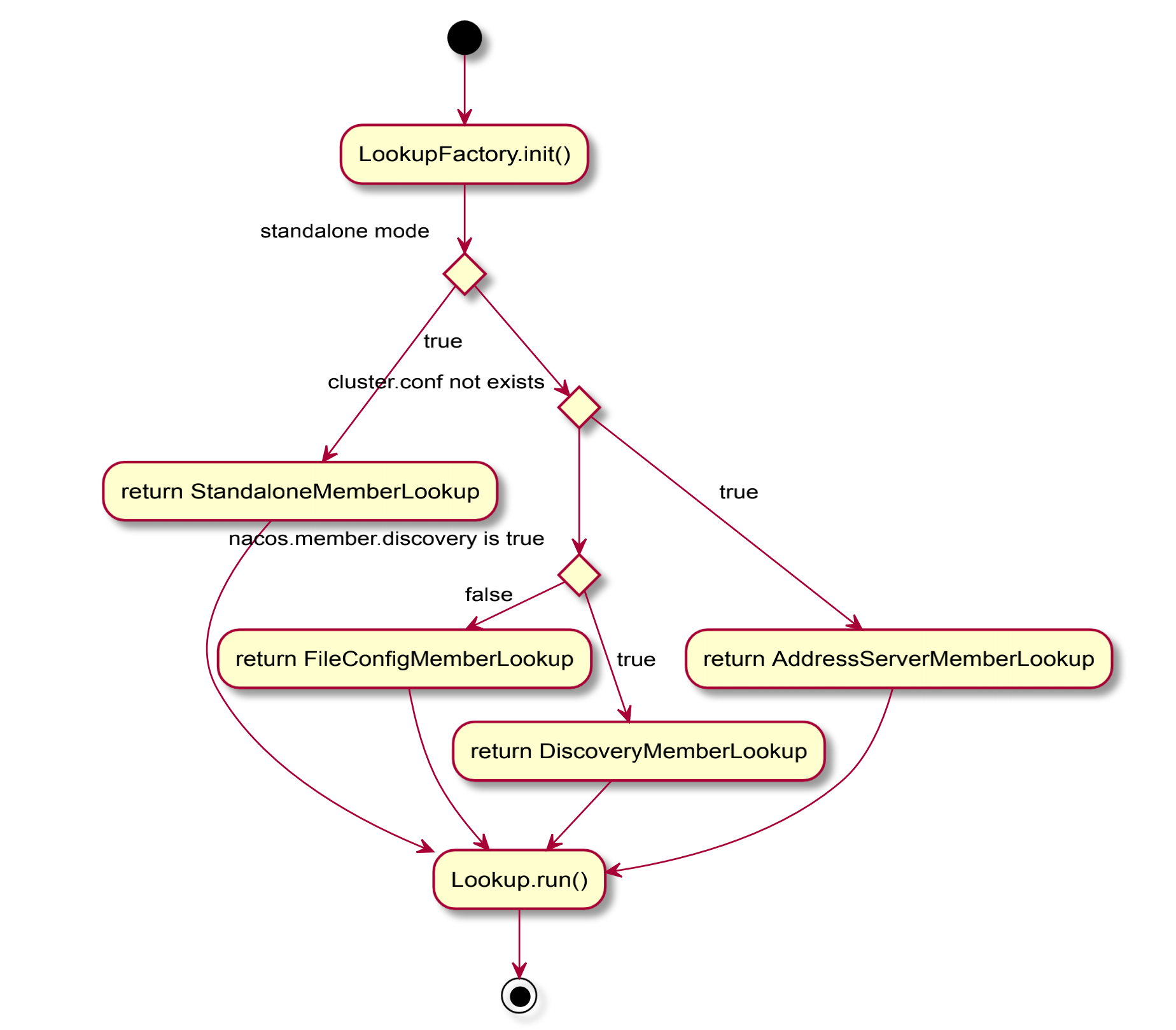 web
web
本次還新增成員節點元數據信息,如site、raft_port、adweight、weight,以支持未來在成員節點之間作相應的負載均衡或者其餘操做,所以cluster.conf 件中配置集羣成員節點列表的格式以下:sql
1172.20.10.7:7001?raft_port=8001&site=unknown&adweight=0&weight=1
該格式徹底兼容本來的cluster.conf格式,用戶在使用 1.3.0-BETA版本時, 無需改動cluster.conf 文件的內容。shell
尋址模式詳細
接下來介紹除了單機模式下的尋址模式的其餘三種尋址模式數據庫
FileConfigMemberLookup
該尋址模式是基於cluster.conf文件進行管理的,每一個節點會讀取各${nacos.home}/conf下的cluster.conf 件內的成員節點列表,而後組成一個集羣。而且在首次讀取完${nacos.home}/conf下的cluster.conf文件後,會自動向操做系統的inotify機制註冊一個目錄監聽器,監聽${nacos.home}/conf目錄下的全部文件變更(注意,這裏只會監聽文件,對於目錄下的文件變更沒法監聽),當須要進行集羣節點擴縮容時,須要手動去修改每一個節點各自${nacos.home}/conf下的cluster.conf的成員節點列表內容。數組
private FileWatcher watcher = new FileWatcher() {
@Override
public void onChange(FileChangeEvent event) {
readClusterConfFromDisk();
}
@Override
public boolean interest(String context) {
return StringUtils.contains(context, "cluster.conf");
}
};
@Override
public void run() throws NacosException {
readClusterConfFromDisk();
if (memberManager.getServerList().isEmpty()) {
throw new NacosException(NacosException.SERVER_ERROR,
"Failed to initialize the member node, is empty" );
}
// Use the inotify mechanism to monitor file changes and automat ically
// trigger the reading of cluster.conf
try {
WatchFileCenter.registerWatcher(ApplicationUtils.getConfFile Path(), watcher);
}
catch (Throwable e) {
Loggers.CLUSTER.error("An exception occurred in the launch f ile monitor : {}", e);
}
}
首次啓動時直接讀取cluster.conf文件內的節點列表信息,而後向WatchFileCenter註冊一個目錄監聽器,當cluster.conf 文件發生變更時自動觸發readClusterConfFromDisk()從新讀取cluster.conf文件。
AddressServerMemberLookup
該尋址模式是基於一個額外的web服務器來管理cluster.conf,每一個節點按期向該web服務器請求cluster.conf的文件內容,而後實現集羣節點間的尋址,以及擴縮容。
當須要進行集羣擴縮容時,只須要修改cluster.conf文件便可,而後每一個節點向地址服務器請求時會自動獲得最新的cluster.conf文件內容。
public void init(ServerMemberManager memberManager) throws NacosExce ption {
super.init(memberManager);
initAddressSys();
this.maxFailCount =Integer.parseInt(ApplicationUtils.getProperty("maxHealthCheckFailCount", "12"));
}
private void initAddressSys() {
String envDomainName = System.getenv("address_server_domain");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(envDomainName)) {
domainName = System.getProperty("address.server.domain", "jm env.tbsite.net");
} else {
domainName = envDomainName;
}
String envAddressPort = System.getenv("address_server_port");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(envAddressPort)) {
addressPort = System.getProperty("address.server.port", "8080");
} else {
addressPort = envAddressPort;
}
addressUrl = System.getProperty("address.server.url", memberManager.getContextPath() + "/" + "serverlist");
addressServerUrl = "http://" + domainName + ":" + addressPort + addressUrl;envIdUrl = "http://" + domainName + ":" + addressPort + "/env";
Loggers.CORE.info("ServerListService address-server port:" + addressPort);
Loggers.CORE.info("ADDRESS_SERVER_URL:" + addressServerUrl);
}
@SuppressWarnings("PMD.UndefineMagicConstantRule")
@Override
public void run() throws NacosException {
// With the address server, you need to perform a synchronous me mber node pull at startup
// Repeat three times, successfully jump out
boolean success = false;
Throwable ex = null;
int maxRetry = ApplicationUtils.getProperty("nacos.core.address-server.retry", Integer.class, 5);
for (int i = 0; i < maxRetry; i ++) {
try {
syncFromAddressUrl();
success = true;
break;
} catch (Throwable e) {
ex = e;
Loggers.CLUSTER.error("[serverlist] exception, error : {}", ex);
}
}
if (!success) {
throw new NacosException(NacosException.SERVER_ERROR, ex);;
}
task = new AddressServerSyncTask();
GlobalExecutor.scheduleSyncJob(task, 5_000L);
}
在初始化時,會主動去向地址服務器同步當前的集羣成員列表信息,若是失敗則進行重試,其最大重試次數可經過設置nacos.core.address-server.retry來控制,默認是5次,而後成功以後,將建立定時任務去向地址服務器同步集羣成員節點信息。
DiscoveryMemberLookup
該尋址模式是新增的集羣節點發現模式,該模式須要cluster.conf或者-Dnacos.member.list提供初始化集羣節點列表,假設已有集羣cluster-one中有A、B、C三個節點,新節點D要加集羣,那麼只須要節點D在啓動時的集羣節點列表存在A、B、C三個中的一個便可,而後節點之間會相互同步各自知道的集羣節點列表,在必定的是時間內,A、B、C、D四個節點知道的集羣節點成員列表都會是[A、B、C、D]在執行集羣節點列表同步時,會隨機選取K個處於UP狀態的節點進行同步。
Collection<Member> members = MemberUtils.kRandom(memberManager, membe r -> {
// local node or node check failed will not perform task processing
if (memberManager.isSelf(member) || !member.check ()) {
return false;
}
NodeState state = member.getState();
return !(state == NodeState.DOWN || state == Node State.SUSPICIOUS);
});
經過一個簡單的流程圖看下DiscoveryMemberLookup是怎麼工做的
圖片正在加載中。。。
RPC端口協商
因爲未來Nacos會對總體通訊通道作升級,採用GRPC優化nacos-server之間,nacos-client與nacos-server之間的通訊,同時爲了兼容目前已有的HTTP協議接口,那麼勢必會帶來這個問題,本機用於RPC協議的端口如何讓其餘節點知道?這裏有兩個解決方案。
從新設計cluster.conf
以前的cluster.conf格式
ip[:port] ip[:port] ip[:port]
因爲nacos默認端口是8848,所以在端口未被修改的狀況下,能夠直接寫IP列表
新的cluster.conf
ip[:port][:RPC_PORT] ip[:port][:RPC_PORT] ip[:port][:RPC_PORT]
對於以前的cluster.conf是徹底支持的,由於nacos內部能夠經過一些計算來約定RPC_PORT的端口值,也能夠經過顯示的設置來約定。經過計算來約定RPC_PORT的代碼以下:
// member port int port = Member.getPort(); // Set the default Raft port information for security int rpcPort = port + 1000 >= 65535 ? port + 1 : port + 1000;
可是這樣會有一個問題,即若是用戶手動設置了RPC_PORT的話,那麼對於客戶端、服務端來講,感知新的RPC_PORT就要修改對應的配置文件或者初始化參數。所以但願說可以讓用戶無感知的過渡到RPC_PORT通訊通道,即用戶須要對RPC協議使用的端口無需本身在進行設置。
端口協商
端口協商即利用目前已有的HTTP接口,將RPC協議佔用的端口經過HTTP接口進行查詢返回,這樣不管是客戶端仍是服務端,都無需修改目前已有的初始化參數或者cluster.conf文件,其大體時序圖以下:

經過一個額外的端口獲取HTTP接口,直接在內部實現RPC端口的協商,而且只會在初始化時進行拉取,這樣,未來nacos新增任何一種協議的端口都無需修改相應的配置信息,自動完成協議端口的感知。
Nacos一致性協議協議層抽象
從nacos的將來的總體架構圖能夠看出,一致性協議層將是做爲nacos的最爲核心的模塊,將服務於構建在core模塊之上的各個功能模塊,或者服務與core模塊自己。而一致性協議由於分區容錯性的存在,須要在可用性與一致性之間作選擇,所以就存在兩大類一致性:最終一致性和強一致性。在nacos中,這兩類致性協議都是可能用到的,好比naming模塊,對於服務實例的數據管理分別用到了AP以及CP,而對於config模塊,將會涉及使用CP。同時還有以下幾個功能需求點:
- 目前持久化服務使用了變種版本的raft,而且業務和raft協議耦合,所以須要抽離解耦,同時是選擇一個標準的Java版Raft實現。
- 對於中小用戶,配置基本不超過100個,獨立一個mysql,相對重一些,須要一個輕量化的存儲方案,而且支持2.0不依賴mysql和3.0依賴mysql可配置能力。
- 因爲CP或者AP,其存在多種實現,如何對一致性協議層作一次很好的抽象,以便未來能夠快速的實現底層一致性協議具體實現的替換,如Raft協議,目前nacos的選型是JRaft,不排除未來nacos會本身實現一個標準raft協議或者實現Paxos協議。
- 因爲Nacos存在多個獨立工做的功能模塊,每一個功能模塊之間不能出現影響,好比A模塊處理請求過慢或者出現異常時,不能影響B模塊的正常工做,即每一個功能模塊在使用一致性協議時,如何將每一個模塊的數據處理進行隔離?
根據一致協議以及上述功能需求點,本次作了一個抽象的一致協議層以及相關的接口。
一致協議接口:ConsistencyProtocol
所謂一致性,即多個副本之間是否可以保持一致性的特性,而副本的本質就是數據,對數據的操做,不是獲取就是修改。同時,一致協議實際上是針對分佈式狀況的,而這必然涉及多個節點,所以,須要有相應的接口可以調整一致性協議的協同工做節點。若是咱們要觀察一致性協議運行的狀況,該怎麼辦?好比Raft協議,咱們但願得知當前集羣中的Leader是誰,任期的狀況,當前集羣中的成員節點有誰?所以,還須要提供一個一致性協議元數據獲取。
綜上所述,ConsistencyProtcol的大體設計能夠出來了
/**
* Has nothing to do with the specific implementation of the consist ency protocol
* Initialization sequence: init(Config)
*
* <ul>
* <li>{@link Config} : Relevant configuration information requi red by the consistency protocol,
* for example, the Raft protocol needs to set the election time out time, the location where
* the Log is stored, and the snapshot task execution interval</ li>
* <li>{@link ConsistencyProtocol#protocolMetaData()} : Returns metadata information of the consistency
* protocol, such as leader, term, and other metadata informatio n in the Raft protocol</li>
* </ul>
*
* @author <a href="mailto:liaochuntao@live.com">liaochuntao</a>
*/
public interface ConsistencyProtocol<T extends Config> extends CommandOperations {
/**
* Consistency protocol initialization: perform initialization o perations based
on the incoming Config
* 一致性協議初始化,根據 Config 實現類
*
* @param config {@link Config}
*/
void init(T config);
/**
* Copy of metadata information for this consensus protocol
* 該一致性協議的元數據信息
*
* @return metaData {@link ProtocolMetaData}
*/
ProtocolMetaData protocolMetaData();
/**
* Obtain data according to the request
* 數據獲取操做,根據GetRequest中的請求上下文進行查詢相應的數據
*
* @param request request
* @return data {@link GetRequest}
* @throws Exception
*/
GetResponse getData(GetRequest request) throws Exception;
/**
* Data operation, returning submission results synchronously
* 同步數據提交,在 Datum 中已攜帶相應的數據操做信息
*
* @param data {@link Log}
* @return submit operation result
* @throws Exception
*/
LogFuture submit(Log data) throws Exception;
/**
* Data submission operation, returning submission results async hronously
* 異步數據提交,在 Datum 中已攜帶相應的數據操做信息,返回一個Future,自行操做,提交發 的異常會在CompleteFuture中
*
* @param data {@link Log}
* @return {@link CompletableFuture<LogFuture>} submit result
* @throws Exception when submit throw Exception
*/
CompletableFuture<LogFuture> submitAsync(Log data);
/**
* New member list
* 新的成員節點列表,一致性協議處理相應的成員節點是加入仍是離開
*
* @param addresses [ip:port, ip:port, ...]
*/
void memberChange(Set<String> addresses);
/**
* Consistency agreement service shut down
* 一致性協議服務關閉
*/
void shutdown();
}
針對CP協議,因爲存在Leader的概念,所以須要提供一個方法用於獲取CP協議當前的Leader是誰
public interface CPProtocol<C extends Config> extends ConsistencyPro tocol<C> {
/**
* Returns whether this node is a leader node
*
* @param group business module info
* @return is leader
* @throws Exception
*/
boolean isLeader(String group) throws Exception;
}
數據操做請求提交對象:Log、GetRequest
上面說到,一致性協議實際上是對於數據操做而言的,數據操做基本分爲兩大類:數據查詢以及數據修改,同時還要知足不一樣功能模塊之間的數據進行隔離。所以這裏針對數據修改操做以及數據查詢操做分別闡述。
1. 數據修改
- 數據修改操做,必定要知道本次請求是屬於哪個功能模塊的。
- 數據修改操做,首先必定要知道這個數據的修改操做具體是哪種修改操做,方便功能模塊針對真正的數據修改操做進行相應的邏輯操做。
- 數據修改操做,必定要知道修改的數據是什麼,即請求體,爲了使得一致性協議層更爲通用,這裏對於請求體的數據結構,選擇了byte[]數組。
- 數據的類型,因爲咱們將真正的數據序列化爲了byte[]數組,爲了可以正常序列化,咱們可能還須要記錄這個數據的類型是什麼。
- 本次請求的信息摘要或者標識信息。
- 本次請求的額外信息,用於未來擴展須要傳輸的數據
綜上,能夠得出Log對象的設計以下:
message Log {
// 功能模塊分組信息
string group = 1;
// 摘要或者標識
string key = 2;
// 具體請求數據
bytes data = 3;
// 數據類型
string type = 4;
// 更爲具體的數據操做
string operation = 5;
// 額外信息
map<string, string> extendInfo = 6;
}
2. 數據查詢
- 數據查詢操做,必定要知道本次請求是由哪個功能模塊發起的。
- 數據查詢的條件是什麼,爲了兼容各類存儲結構的數據查詢操做,這byte[]進行存儲。
- 本次請求的額外信息,用於未來擴展須要傳輸的數據。
綜上,能夠得出GetRequest對象的設計以下
message GetRequest {
// 功能模塊分組信息
string group = 1;
// 具體請求數據
bytes data = 2;
// 額外信息
map<string, string> extendInfo = 3;
}
功能模塊使一致性協議:LogProcessor
當數據操做經過一致性協議進行submit以後,每一個節點須要去處理這個Log或者GetRequest對象,所以,咱們須要抽象出一個Log、GetRequest對象的Processor,不一樣的功能模塊經過實現該處理器,ConsistencyProtocol內部會根據Log、GetRequest的group屬性,將Log、GetRequest對象路由到具體的Processor,固然,Processor也須要代表本身是屬於哪個功能模塊的。
public abstract class LogProcessor {
/**
* get data by key
*
* @param request request {@link GetRequest}
* @return target type data
*/
public abstract GetResponse getData(GetRequest request);
/**
* Process Submitted Log
*
* @param log {@link Log}
* @return {@link boolean}
*/
public abstract LogFuture onApply(Log log);
/**
* Irremediable errors that need to trigger business price cuts
*
* @param error {@link Throwable}
*/
public void onError(Throwable error) {
}
/**
* In order for the state machine that handles the transaction to be able to route
* the Log to the correct LogProcessor, the LogProcessor needs to have an identity
* information
*
* @return Business unique identification name
*/
public abstract String group();
}
針對CP協議,好比Raft協議,存在快照的設計,所以咱們須要針對CP協議單獨擴展出一個方法。
public abstract class LogProcessor4CP extends LogProcessor {
/**
* Discovery snapshot handler
* It is up to LogProcessor to decide which SnapshotOperate shou ld be loaded and saved by itself
*
* @return {@link List <SnapshotOperate>}
*/
public List<SnapshotOperation> loadSnapshotOperate() {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}
咱們能夠經過一個時序圖看看,一致性協議層的大體工做流程以下:
Nacos一致性協議層之CP協議的實現選擇——JRaft
一致性協議層抽象好以後,剩下就是具體一致性協議實現的選擇了,這裏咱們選擇了螞蟻服開源的JRaft,那麼咱們如何將JRaft做爲CP協議的一個Backend呢?下面的簡單流程圖描述了當JRaft做爲CP協議的一個Backend時的初始化流程。
圖片正在加載中。。。
JRaftProtocol是當JRaft做爲CP協議的Backend時的一個ConsistencyProtocol的具體實現,其內部有一個JRaftServer成員屬性,JRaftServer分裝了JRaft的各類API操做,好比數據操做的提交,數據的查詢,成員節點的變動,Leader節點的查詢等等。
注意事項:JRaft運行期間產生的數據在
${nacos.home}/protocol/raft文件目錄下。不一樣的業務模塊有不一樣的文件分組,若是當節點出現crash或者異常關閉時,清空該目錄下的文件,重啓節點便可。
因爲JRaft實現了raft group的概念,所以,徹底能夠利用 raft group的設計,爲每一個功能模塊單首創建個raft group。這裏給出部分代碼,該代碼體現瞭如何將LogProcessor嵌入到狀態機中併爲每一個LogPrcessor建立一個Raft Group。
synchronized void createMultiRaftGroup(Collection<LogProcessor4CP> processors) {
// There is no reason why the LogProcessor cannot be processed b ecause of the synchronization
if (!this.isStarted) {
this.processors.addAll(processors);
return;
}
final String parentPath = Paths.get(ApplicationUtils.getNacosHome(), "protocol/raft").toString();
for (LogProcessor4CP processor : processors) {
final String groupName = processor.group();
if (alreadyRegisterBiz.contains(groupName)) {
throw new DuplicateRaftGroupException(groupName);
}
alreadyRegisterBiz.add(groupName);
final String logUri = Paths.get(parentPath, groupName, "log").toString();
final String snapshotUri = Paths.get(parentPath, groupName,"snapshot").toString();
final String metaDataUri = Paths.get(parentPath, groupName,"meta-data").toString();
// Initialize the raft file storage path for different services
try {
DiskUtils.forceMkdir(new File(logUri));
DiskUtils.forceMkdir(new File(snapshotUri));
DiskUtils.forceMkdir(new File(metaDataUri));
}
catch (Exception e) {
Loggers.RAFT.error("Init Raft-File dir have some error : {}", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// Ensure that each Raft Group has its own configuration and NodeOptions
Configuration configuration = conf.copy();
NodeOptions copy = nodeOptions.copy();
// Here, the LogProcessor is passed into StateMachine, and when the StateMachine
// triggers onApply, the onApply of the LogProcessor is actually called
NacosStateMachine machine = new NacosStateMachine(this, processor);
copy.setLogUri(logUri);
copy.setRaftMetaUri(metaDataUri);
copy.setSnapshotUri(snapshotUri);
copy.setFsm(machine);
copy.setInitialConf(configuration);
// Set snapshot interval, default 1800 seconds
int doSnapshotInterval = ConvertUtils.toInt(raftConfig.getVal(RaftSysConstants.RAFT_SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL_SECS),
RaftSysConstants.DEFAULT_RAFT_SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL_ SECS);
// If the business module does not implement a snapshot processor, cancel the snapshot
doSnapshotInterval = CollectionUtils.isEmpty(processor.loadS napshotOperate()) ? 0 : doSnapshotInterval;
copy.setSnapshotIntervalSecs(doSnapshotInterval);
Loggers.RAFT.info("create raft group : {}", groupName);
RaftGroupService raftGroupService = new RaftGroupService(gro upName, localPeerId, copy, rpcServer, true);
// Because RpcServer has been started before, it is not allo wed to start again here
Node node = raftGroupService.start(false);
machine.setNode(node);
RouteTable.getInstance().updateConfiguration(groupName, conf iguration);
// Turn on the leader auto refresh for this group
Random random = new Random();
long period = nodeOptions.getElectionTimeoutMs() + random.ne xtInt(5 * 1000);
RaftExecutor.scheduleRaftMemberRefreshJob(() -> refreshRoute Table(groupName), period, period, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// Save the node instance corresponding to the current group
multiRaftGroup.put(groupName, new RaftGroupTuple(node, proce ssor, raftGroupService));
}
}
或許有的人會有疑問,爲何要建立多個raft group,既然以前已經設計出了LogProcessor,徹底能夠利用一個Raft
Group,在狀態機appl時,根據Log的group屬性進行路由到不一樣的LogProcessor便可,每一個功能模塊就建立一個raft group,不是會消耗大量的資源嗎?
正如以前所說,咱們但願獨工做的模塊之間相互不存在影響,好比A模塊處理Log由於存在Block操做可能使得apply的速度緩慢,亦或者可能中途發生異常,對於Raft協議來講,當日志apply失敗時,狀態機將不可以繼續向前推動,由於若是繼續向前推動的話,因爲上一步的apply失敗,後面的全部apply均可能失敗,將會致使這個節點的數據與其餘節點的數據永遠不一致。若是說咱們將全部獨立工做的模塊,對於數據操做的請求處理放在同一個raft group,即一個狀態機中,就不可避免的會出現上述所說的問題,某個模塊在apply 日誌發生不可控的因素時,會影響其餘模塊的正常工做。
JRaft運維操做
爲了使用者可以對JRaft進行相關簡單的運維,如Leader的切換,重置當前Raft集羣成員,觸發某個節點進行Snapshot操做等等,提供了一個簡單的HTTP接口進行操做,而且該接口有必定的限制,即每次只會執行一條運維指令。
1.切換某一個Raft Group的Leader節點
POST /nacos/v1/core/ops/raft
{
"groupId": "xxx",
"transferLeader": "ip:{raft_port}"
}
2.重置某一個Raft Group的集羣成員
POST /nacos/v1/core/ops/raft
{
"groupId": "xxx",
"resetRaftCluster": "ip:{raft_port},ip:{raft_port},ip:{raft_por t},ip:{raft_port}"
}
3.觸發某一個Raft Group執行快照操做
POST /nacos/v1/core/ops/raft
{
"groupId": "xxx",
"doSnapshot": "ip:{raft_port}"
}
JRaft協議相關配置參數
### Sets the Raft cluster election timeout, default value is 5 second nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.election_timeout_ms=5000 ### Sets the amount of time the Raft snapshot will execute periodica lly, default is 30 minute nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.snapshot_interval_secs=30 ### Requested retries, default value is 1 nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.request_failoverRetries=1 ### raft internal worker threads nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.core_thread_num=8 ### Number of threads required for raft business request processing nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.cli_service_thread_num=4 ### raft linear read strategy, defaults to index nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.read_index_type=ReadOnlySafe ### rpc request timeout, default 5 seconds nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.rpc_request_timeout_ms=5000 ### Maximum size of each file RPC (snapshot copy) request between me mbers, default is 128 K nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.max_byte_count_per_rpc=131072 ### Maximum number of logs sent from leader to follower, default is 1024 nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.max_entries_size=1024 ### Maximum body size for sending logs from leader to follower, defa ult is 512K nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.max_body_size=524288 ### Maximum log storage buffer size, default 256K nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.max_append_buffer_size=262144 ### Election timer interval will be a random maximum outside the spe cified time, default is 1 second nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.max_election_delay_ms=1000 ### Specify the ratio between election timeout and heartbeat interval. Heartbeat interval is equal to ### electionTimeoutMs/electionHeartbeatFactor,One tenth by default. nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.election_heartbeat_factor=10 ### The tasks submitted to the leader accumulate the maximum batch s ize of a batch flush log storage. The default is 32 tasks. nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.apply_batch=32 ### Call fsync when necessary when writing logs and meta informatio n, usually should be true nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.sync=true ### Whether to write snapshot / raft meta-information to call fsync. The default is false. When sync is true, it is preferred to respect sync. nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.sync_meta=false ### Internal disruptor buffer size. For applications with high write throughput, you need to increase this value. The default value is 16384. nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.disruptor_buffer_size=16384 ### Whether to enable replication of pipeline request optimization, which is enabled by default nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.replicator_pipeline=true ### Maximum number of in-flight requests with pipeline requests enab led, default is 256 nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.max_replicator_inflight_msgs=256 ### Whether to enable LogEntry checksum nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.enable_log_entry_checksum=false
Nacos內嵌分佈式ID
nacos內嵌的分佈式ID爲Snakeflower,dataCenterId默認爲1,workerId的值計算方式以下:
InetAddress address;
try {
address = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
} catch (final UnknownHostException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot get LocalHost InetAddress, please ch eck your network!");
}
byte[] ipAddressByteArray = address.getAddress();
workerId = (((ipAddressByteArray[ipAddressByteArray.length - 2] & 0B 11)
<< Byte.SIZE) + (ipAddressByteArray[ipAddressByteArray.length - 1] & 0xFF));
若是須要手動指定dataCenterId以及workerId,則在application.properties或者啓動時添加命令 參數
### set the dataCenterID manually # nacos.core.snowflake.data-center= ### set the WorkerID manually # nacos.core.snowflake.worker-id=
Nacos內嵌的輕量的基於Derby的分佈式關係型存儲
背景
- 若是配置文件數量較少,在集羣模式下須要高可用數據庫集羣做爲支撐的成本太大,指望有一個輕量的分佈式關係型存儲來解決。
- nacos內部一些元數據信息存儲,好比用戶信息,命名空間信息
- 思路來源:https://github.com/rqlite/rqlite
設計思路
整體
將一次請求操做涉及的SQL上下文按順序保存起來。而後經過一致協議層將本次請求涉及的SQL上下 文進行同步,而後每一個節點將其解析並從新按順序在一次數據庫會話中執行。

誰能夠處理請求
當使用者開啓1.3.0-BETA的新特性——內嵌分佈式關係型數據存儲時,全部的寫操做請求都將路由到Leader節點進行處理;可是,因爲Raft狀態機的特性,當某一個節點在apply數據庫操做請求時發生非SQL邏輯錯誤引起的異常時,將致使狀態機沒法繼續正常進行工做,此時將會觸發配置管理模塊的降級操做。
private void registerSubscribe() {
NotifyCenter.registerSubscribe(new SmartSubscribe() {
@Override
public void onEvent(Event event) {
if (event instanceof RaftDBErrorRecoverEvent) {
downgrading = false;
return;
}
if (event instanceof RaftDBErrorEvent) {
downgrading = true;
}
}
@Override
public boolean canNotify(Event event) {
return (event instanceof RaftDBErrorEvent) || (event instanceof RaftDBErrorRecoverEvent);
}
});
}
所以,綜上所述,能夠經過活動圖來理解下,什麼狀況下須要將請求進行轉發呢?

相關數據承載對象
數據庫的DML語句是select、insert、update、delete,根據SQL語句對於數據操做的性質,能夠分爲兩類:query以及update,select語句對應的是數據查詢,insert、update、delete語句對應的是數據修改。同時在進行數據庫操做時,爲了不SQL入注,使用的是PreparedStatement,所以須要SQL語句+參數,所以能夠獲得兩個關於數據庫操做的Request對象。
- SelectRequest
public class SelectRequest implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2212052574976898602L;
// 查詢類別,由於 前使 的是JdbcTemplate,查詢單個、查詢多個,是否使 RowM apper轉爲對象
5private byte queryType;
// sql語句
// select * from config_info where
private String sql;
private Object[] args;
private String className;
}
- ModifyRequest
public class ModifyRequest implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4548851816596520564L;
private int executeNo;
private String sql;
private Object[] args;
}
配置發佈
配置發佈操做涉及三個事務:
- config_info保存配置信息。
- config_tags_relation保存配置與標籤的關聯關係。
- his_config_info保存 條配置操做歷史記錄。
這三個事務都在配置發佈這個大事務下,若是說咱們對每一個事務操做進行一個Raft協議提交,假設一、2兩個事務經過Raft提交後都成功Apply了,第三個事務在進行Raft提交後apply失敗,那麼對於這個配置發佈的大事務來講,是須要總體回滾的,不然就會違反原子性,那麼可能須要說將事務回滾操做又進行一次Raft提交,那麼總體的複雜程度上升,而且直接引了分佈式事務的管理,所以爲了不這個問題,咱們將這三個事務涉及的SQL上下文進行整合成一個大的SQL上下文,對這大的SQL上下文進行Raft協議提交。保證了三個子事務在同一次數據庫會話當中,成功解決原子性的問題,同時因爲Raft協議對於事務日誌的處理是串行執行的,所以至關於將數據庫的事務隔離級別調整爲串行化。
public void addConfigInfo(final String srcIp, final String srcUser,
final ConfigInfo configInfo, final Timestamp time,
final Map<String, Object> configAdvanceInfo, final boolean notify) {
try {
// 同過雪花ID獲取一個ID值
long configId = idGeneratorManager.nextId(configInfoId);
long configHistoryId = idGeneratorManager.nextId(this.configHistoryId);
// 配置插入
addConfigInfoAtomic(configId, srcIp, srcUser, configInfo, time, configAdvanceInfo);
String configTags = configAdvanceInfo == null ? null : (String) configAdvanceInfo.get("config_tags");
// 配置與標籤信息關聯操做
addConfigTagsRelation(configId, configTags, configInfo.getD ataId(), configInfo.getGroup(), configInfo.getTenant());
// 配置歷史插入
insertConfigHistoryAtomic(configHistoryId, configInfo, srcI p, srcUser, time, "I");
boolean result = databaseOperate.smartUpdate();
if (!result) {
throw new NacosConfigException("Config add failed");
}
if (notify) {
EventDispatcher.fireEvent(
new ConfigDataChangeEvent(false, configInfo.getDataId(),
configInfo.getGroup(), configInfo.getTenant(), time.getTime()));
}
}
finally {
SqlContextUtils.cleanCurrentSqlContext();
}
}
public long addConfigInfoAtomic(final long id, final String srcIp, final String srcUser, final ConfigInfo configInfo, final Timestamp time, Map<String, Object> configAdvanceInfo) {
...
// 參數處理
...
final String sql =
"INSERT INTO config_info(id, data_id, group_id, tenant_id, app_name, content, md5, src_ip, src_user, gmt_create,"
+ "gmt_modified, c_desc, c_use, effect, type, c_schema) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";
final Object[] args = new Object[] { id, configInfo.getDataId(),
configInfo.getGroup(), tenantTmp, appNameTmp, configInfo.getContent(),
md5Tmp, srcIp, srcUser, time, time, desc, use, effect, type, schema, };
SqlContextUtils.addSqlContext(sql, args);
return id;
}
public void addConfigTagRelationAtomic(long configId, String tagName, String dataId,
String group, String tenant) {
final String sql = "INSERT INTO config_tags_relation(id,tag_name,tag_type,data_id,group_id,tenant_id) " + "VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?)";
final Object[] args = new Object[] { configId, tagName, null, d ataId, group, tenant };
SqlContextUtils.addSqlContext(sql, args);
}
public void insertConfigHistoryAtomic(long configHistoryId, ConfigI nfo configInfo, String srcIp, String srcUser, final Timestamp time, String ops) {
...
// 參數處理
...
final String sql = "INSERT INTO his_config_info (id,data_id,group_id,tenant_id,app_name,content,md5," + "src_ip,src_user,gmt_modified,op_type) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";
final Object[] args = new Object[] { configHistoryId, configInf o.getDataId(), configInfo.getGroup(), tenantTmp, appNameTmp, configInfo.getContent(), md5Tmp, srcIp, srcUser, time, ops};
SqlContextUtils.addSqlContext(sql, args);
}
/**
* Temporarily saves all insert, update, and delete statements under
* a transaction in the order in which they occur
*
* @author <a href="mailto:liaochuntao@live.com">liaochuntao</a>
*/
public class SqlContextUtils {
private static final ThreadLocal<ArrayList<ModifyRequest>> SQL_CONTEXT =
ThreadLocal.withInitial(ArrayList::new);
public static void addSqlContext(String sql, Object... args) {
ArrayList<ModifyRequest> requests = SQL_CONTEXT.get();
ModifyRequest context = new ModifyRequest();
context.setExecuteNo(requests.size());
context.setSql(sql);
context.setArgs(args);
requests.add(context);
SQL_CONTEXT.set(requests);
}
public static List<ModifyRequest> getCurrentSqlContext() {
return SQL_CONTEXT.get();
}
public static void cleanCurrentSqlContext() {
SQL_CONTEXT.remove();
}
}
經過一個時序圖來更加直觀的理解

如何使用新特性
#*************** Embed Storage Related Configurations *************** # ### This value is true in stand-alone mode and false in cluster mode ### If this value is set to true in cluster mode, nacos's distributed storage engine is turned on embeddedStorage=true
是否啓用內嵌的分佈式關係型存儲的活動圖

新特性的相關運維操做
直接查詢每一個節點的derby存儲的數據
GET /nacos/v1/cs/ops/derby?sql=select * from config_info
return List<Map<String, Object>>
不足
- 在數據庫上層構建一層分佈式數據操做同步層,對數據庫的操做存在了限制,如第一步insert操做,而後select操做,最後在update操做,這種在數據修改語句中穿插着查詢語句的操做順序是不支持的。
- 限制了數據庫的性能,因爲間接的將數據庫事務隔離級別調整爲了串行化,人爲的將併發能力下降了。
將來演進
將於Apache Derby官方一塊兒嘗試基於Raft實現BingLog的同步複製操做,從底層實現數據庫同步能力。

- 1. 一大波碩士即未來襲
- 2. 一波黑科技即將襲來!StarVR帶你感受他們的未來
- 3. WWDC2015 結束.新一波更新以及bug即未來襲.
- 4. 該來的都來了 美光一大波SSD新品襲來
- 5. 「指尖上的華爾茲」--Leap Motion 2015在線開發大賽即未來襲!
- 6. 2020年即未來臨
- 7. Nuxt 2 即未來臨
- 8. 抄襲-寫給未來的自己
- 9. 虛幻5引擎即將來襲
- 10. SuperVOOC加持,OPPO R17 Pro即將來襲
- 更多相關文章...
- • DTD - 來自網絡的實例 - DTD 教程
- • Docker 命令大全 - Docker教程
- • 互聯網組織的未來:剖析GitHub員工的任性之源
- • JDK13 GA發佈:5大特性解讀
-
每一个你不满意的现在,都有一个你没有努力的曾经。