# webpack 打包工具(vue)
vue-webpack 打包工具
個人github iSAM2016
不是教程,是自我總結css
目錄
一開始在接觸webpack 的時候,簡直痛不欲生,如今回頭看,作個註釋,
固然參考了不少文章。這是一個關於vue 開發的webpack 架構會列舉出來
webpack 系列教程
Webpack——使人困惑的地方
Express結合Webpack的全棧自動刷新
Webpack傻瓜式指南(一)
Webpack資源總結html
啓動指令vue
"scripts": {
"dev": "node build/dev-server.js", //
"build": "node build/build.js",// 打包
"lint": "eslint --ext .js,.vue src"
},
webpack.base.conf.js
webpack基本配置node
var path = require('path')
var config = require('../config')
var utils = require('./utils')
var projectRoot = path.resolve(__dirname, '../')
var env = process.env.NODE_ENV
// check env & config/index.js to decide whether to enable CSS source maps for the
// various preprocessor loaders added to vue-loader at the end of this file
var cssSourceMapDev = (env === 'development' && config.dev.cssSourceMap)
var cssSourceMapProd = (env === 'production' && config.build.productionSourceMap)
var useCssSourceMap = cssSourceMapDev || cssSourceMapProd
// 配置文件的內容須要經過module.exports暴露
module.exports = {
// 配置須要打包的入口文件,值能夠是字符串、數組、對象。
// 1. 字符串: entry: './entry'
// 2. 字符串: entry:[ './entry1','entry2'] (多入口)
// 3. 對象: entry: {alert/index': path.resolve(pagesDir, `./alert/index/page`)}
// 多入口書寫的形式應爲object,由於object,的key在webpack裏至關於此入口的name,
entry: {
app: './src/main.js'
},
output: {
// 輸出文件配置,output 輸出有本身的一套規則,經常使用的參數基本就是這三個
// path: 表示生成文件的根目錄 須要一個**絕對路徑** path僅僅告訴Webpack結果存儲在哪裏
path: config.build.assetsRoot,
// publicPath 參數表示的是一個URL 路徑(指向生成文件的跟目錄),用於生成css/js/圖片/字體文件
// 等資源的路徑以確保網頁能正確地加載到這些資源.
// 「publicPath」項則被許多Webpack的插件用於在生產模式下更新內嵌到css、html文件裏的url值.
// 例如,在localhost(即本地開發模式)裏的css文件中邊你可能用「./test.png」這樣的url來加載圖片,
// 可是在生產模式下「test.png」文件可能會定位到CDN上而且你的Node.js服務器多是運行在HeroKu上邊的。
// 這就意味着在生產環境你必須手動更新全部文件裏的url爲CDN的路徑。
//開發環境:Server和圖片都是在localhost(域名)下
//.image {
// background-image: url('./test.png');
//}
// 生產環境:Server部署下HeroKu可是圖片在CDN上
//.image {
// background-image: url('https://someCDN/test.png');
//}
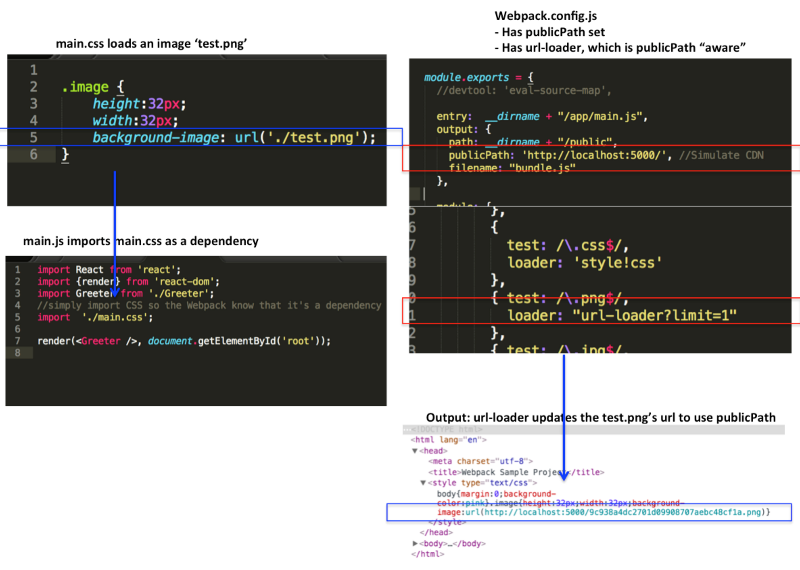
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? config.build.assetsPublicPath : config.dev.assetsPublicPath,
// filename 屬性表示的是如何命名出來的入口文件,規則是一下三種:
// [name] 指代入口文件的name,也就是上面提到的entry參數的key,所以,咱們能夠在name裏利用/,便可達到控制文件目錄結構的效果。
// [hash],指代本次編譯的一個hash版本,值得注意的是,只要是在同一次編譯過程當中生成的文件,這個[hash].js
//的值就是同樣的;在緩存的層面來講,至關於一次全量的替換。
filename: '[name].js'
},
// 用來配置依賴文件的匹配,如依賴文件的別名配置、模塊的查找目錄、默認查找的
// 文件後綴名
// resolve.root 該選型用來制定模塊查找的根路徑,必須爲**絕對路徑**,值能夠
// 是路徑字符串或者路徑數組如果數組,則會依次查找
resolve: {
extensions: ['', '.js', '.vue', '.json'],
fallback: [path.join(__dirname, '../node_modules')],
// 用來配置依賴文件的別名,值是一個對,該對象的鍵是別名,值是實際路徑
alias: {
'vue$': 'vue/dist/vue.common.js',
'src': path.resolve(__dirname, '../src'),
'assets': path.resolve(__dirname, '../src/assets'),
'components': path.resolve(__dirname, '../src/components')
}
},
resolveLoader: {
fallback: [path.join(__dirname, '../node_modules')]
},
// 用來進行模塊加載相關的配置
module: {
preLoaders: [
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'eslint',
include: projectRoot,
exclude: /node_modules/
},
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'eslint',
include: projectRoot,
exclude: /node_modules/
}
],
loaders: [
// webpack擁有一個相似於插件的機制,名爲Loader,經過Loader,webpack可以針對每一種特定的資源作出相應的處理
// 1.test參數用來指示當前配置項針對哪些資源,該值應是一個條件值(condition)。
// 2.exclude參數用來剔除掉須要忽略的資源,該值應是一個條件值(condition)。
// 3.include參數用來表示本loader配置僅針對哪些目錄/文件,該值應是一個條件值(condition)。
// 而include參數則用來指示目錄;注意同時使用這二者的時候,其實是and的關係。
// 4.loader/loaders參數,用來指示用哪一個或哪些loader來處理目標資源,這倆貨
// 表達的實際上是一個意思,只是寫法不同,我我的推薦用loader寫成一行,多個
// loader間使用!分割,這種形式相似於管道的概念,又或者說是函數式編程。形
// 如loader: 'css?!postcss!less',能夠很明顯地看出,目標資源先經less-loader
// 處理事後將結果交給postcss-loader做進一步處理,而後最後再交給css-loader。
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue'
},
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel',
include: projectRoot,
exclude: /node_modules/
},
{
test: /\.json$/,
loader: 'json'
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url',
query: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('img/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
{
test: /\.(woff2?|eot|ttf|otf)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url',
query: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('fonts/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
// expose-loader,這個loader的做用是,將指定js模塊export的變量聲明爲全局變量
{
test: require.resolve('jquery'), // 此loader配置項的目標是NPM中的jquery
loader: 'expose?$!expose?jQuery', // 先把jQuery對象聲明成爲全局變量`jQuery`,再經過管道進一步又聲明成爲全局變量`$`
},
]
},
eslint: {
formatter: require('eslint-friendly-formatter')
},
vue: {
loaders: utils.cssLoaders({ sourceMap: useCssSourceMap }),
// 解決.vue中文件style的部分一些特性解析,好比scoped
postcss: [
require('autoprefixer')({
browsers: ['last 2 versions']
})
]
}
}
webpack.dev.conf.js
var config = require('../config')
var webpack = require('webpack')
var merge = require('webpack-merge')
var utils = require('./utils')
var baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf')
var HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
// add hot-reload related code to entry chunks
Object.keys(baseWebpackConfig.entry).forEach(function (name) {
baseWebpackConfig.entry[name] = ['./build/dev-client'].concat(baseWebpackConfig.entry[name])
})
module.exports = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {
module: {
loaders: utils.styleLoaders({ sourceMap: config.dev.cssSourceMap })
},
// eval-source-map is faster for development
devtool: '#eval-source-map',
plugins: [
// DefinePlugin 是webpack 的內置插件,該插件能夠在打包時候替換制定的變量
//
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': config.dev.env
}),
// https://github.com/glenjamin/webpack-hot-middleware#installation--usage
new webpack.optimize.OccurrenceOrderPlugin(),
new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin(),
new webpack.NoErrorsPlugin(),
// https://github.com/ampedandwired/html-webpack-plugin
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: 'index.html',
template: 'index.html',
inject: true
}),
// 能夠自動加載當前模塊依賴的其餘模塊並已制定別名注入到當前的模塊中,引入jq
// 在網上看到的文章,救了個人命 ProvidePlugin + expose-loader 引入jq
//
// 若是你把jQuery看作是一個普通的js模塊來加載(要用到jQuery的模塊通通先require
// 後再使用),那麼,當你加載老式jQuery插件時,每每會提示找不到jQuery實例
// 有時候是提示找不到$),這是爲啥呢?
// 要解釋這個問題,就必須先稍微解釋一下jQuery插件的機制:jQuery插件是經過
// jQuery提供的jQuery.fn.extend(object)和jQuery.extend(object)這倆方法,來
// 把插件自己實現的方法掛載到jQuery(也即$)這個對象上的。傳統引用jQuery及
// 其插件的方式是先用<script>加載jQuery自己,而後再用一樣的方法來加載其插件;
// jQuery會把jQuery對象設置爲全局變量(固然也包括了$),既然是全局變量,那麼
// 插件們很容易就能找到jQuery對象並掛載自身的方法了。
//
// 而webpack做爲一個聽從模塊化原則的構建工具,天然是要把各模塊的上下文環境給
// 分隔開以減小相互間的影響;而jQuery也早已適配了AMD/CMD等加載方式,換句話說,
// 咱們在require jQuery的時候,實際上並不會把jQuery對象設置爲全局變量。說到
// 這裏,問題也很明顯了,jQuery插件們找不到jQuery對象了,由於在它們各自的上下
// 文環境裏,既沒有局部變量jQuery(由於沒有適配AMD/CMD,因此就沒有相應的requi
// re語句了),也沒有全局變量jQuery。
//
// A: ProvidePlugin的機制是:當webpack加載到某個js模塊裏,出現了未定義且名稱符合
// (字符串徹底匹配)配置中key的變量時,會自動require配置中value所指定的js模塊
// expose-loader,這個loader的做用是,將指定js模塊export的變量聲明爲全局變量。
//
// B:externals 調用jq
// externals是webpack配置中的一項,用來將某個全局變量「假裝」成某個js模塊的exports,
// 以下面這個配置:
// externals: {'jquery': 'window.jQuery',},
// 那麼,當某個js模塊顯式地調用var $ = require('jquery')的時候,就會把window,
// jQuery返回給它,與上述ProvidePlugin + expose-loader的方案相反,此方案是先用
// <script>加載的jQuery知足老式jQuery插件的須要,再經過externals將其轉換成符合
// 模塊化要求的exports。
new webpack.ProvidePlugin({
$: "jquery",
jQuery: "jquery",
"window.jQuery": "jquery",
'window.$': 'jquery',
})
]
})
webpack.prod.conf.js
var path = require('path')
var config = require('../config')
var utils = require('./utils')
var webpack = require('webpack')
var merge = require('webpack-merge')
var baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf')
var ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin')
var HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
var env = config.build.env
var webpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {
module: {
loaders: utils.styleLoaders({ sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap, extract: true })
},
devtool: config.build.productionSourceMap ? '#source-map' : false,
output: {
path: config.build.assetsRoot,
filename: utils.assetsPath('js/[name].[chunkhash].js'),
chunkFilename: utils.assetsPath('js/[id].[chunkhash].js')
},
vue: {
loaders: utils.cssLoaders({
sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap,
extract: true
})
},
// webpack插件位置,有固定的用法
// 1. 利用Plugin的初始方法並傳入Plugin預設的參數進行初始化,生成一個實例。
// 2. 將此實例插入到webpack配置文件中的plugins參數(數組類型)裏便可。
//
// 1.
plugins: [
// http://vuejs.github.io/vue-loader/en/workflow/production.html
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': env
}),
new webpack.optimize.UglifyJsPlugin({
compress: {
warnings: false
}
}),
new webpack.optimize.OccurrenceOrderPlugin(),
// extract css into its own file
new ExtractTextPlugin(utils.assetsPath('css/[name].[contenthash].css')),
// generate dist index.html with correct asset hash for caching.
// you can customize output by editing /index.html
// see https://github.com/ampedandwired/html-webpack-plugin
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
// filename 生成網頁的HTML名字,可使用/來控制文件文件的目錄結構,最
// 終生成的路徑是基於webpac配置的output.path的
filename: config.build.index,
template: 'index.html',
inject: true,
// inject,指示把加載js文件用的<script>插入到哪裏,默認是插到<body>
// 的末端,若是設置爲'head',則把<script>插入到<head>裏。
minify: {
removeComments: true,
collapseWhitespace: true,
removeAttributeQuotes: true
// more options:
// https://github.com/kangax/html-minifier#options-quick-reference
},
// necessary to consistently work with multiple chunks via CommonsChunkPlugin
chunksSortMode: 'dependency'
}),
// 若是文件是多入口的文件,可能存在,重複代碼,把公共代碼提取出來,又不會重複下載公共代碼了
// (多個頁面間會共享此文件的緩存)
// CommonsChunkPlugin的初始化經常使用參數有解析?
// name: 這個給公共代碼的chunk惟一的標識
// filename,如何命名打包後生產的js文件,也是能夠用上[name]、[hash]、[chunkhash]
// minChunks,公共代碼的判斷標準:某個js模塊被多少個chunk加載了纔算是公共代碼
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'vendor',
minChunks: function (module, count) {
// any required modules inside node_modules are extracted to vendor
return (
module.resource &&
/\.js$/.test(module.resource) &&
module.resource.indexOf(
path.join(__dirname, '../node_modules')
) === 0
)
}
}),
// extract webpack runtime and module manifest to its own file in order to
// prevent vendor hash from being updated whenever app bundle is updated
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'manifest',
chunks: ['vendor']
})
]
})
if (config.build.productionGzip) {
var CompressionWebpackPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
webpackConfig.plugins.push(
new CompressionWebpackPlugin({
asset: '[path].gz[query]',
algorithm: 'gzip',
test: new RegExp(
'\\.(' +
config.build.productionGzipExtensions.join('|') +
')$'
),
threshold: 10240,
minRatio: 0.8
})
)
}
module.exports = webpackConfig
相關文章
- 1. webpack打包工具
- 2. Webpack(打包工具)
- 3. Webpack 打包工具
- 4. vue之webpack打包工具的使用
- 5. vue 之webpack打包工具的使用
- 6. webpack前端打包工具
- 7. webpack打包工具理解
- 8. 4、webpack打包工具
- 9. Webpack前端打包工具
- 10. [vue]webpack打包
- 更多相關文章...
- • jQuery Mobile 工具欄 - jQuery Mobile 教程
- • netwox網絡工具集入門教程 - TCP/IP教程
- • PHP開發工具
- • IDEA下SpringBoot工程配置文件沒有提示
相關標籤/搜索
每日一句
-
每一个你不满意的现在,都有一个你没有努力的曾经。
最新文章
- 1. 「插件」Runner更新Pro版,幫助設計師遠離996
- 2. 錯誤 707 Could not load file or assembly ‘Newtonsoft.Json, Version=12.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKe
- 3. Jenkins 2018 報告速覽,Kubernetes使用率躍升235%!
- 4. TVI-Android技術篇之註解Annotation
- 5. android studio啓動項目
- 6. Android的ADIL
- 7. Android卡頓的檢測及優化方法彙總(線下+線上)
- 8. 登錄註冊的業務邏輯流程梳理
- 9. NDK(1)創建自己的C/C++文件
- 10. 小菜的系統框架界面設計-你的評估是我的決策
歡迎關注本站公眾號,獲取更多信息

相關文章
- 1. webpack打包工具
- 2. Webpack(打包工具)
- 3. Webpack 打包工具
- 4. vue之webpack打包工具的使用
- 5. vue 之webpack打包工具的使用
- 6. webpack前端打包工具
- 7. webpack打包工具理解
- 8. 4、webpack打包工具
- 9. Webpack前端打包工具
- 10. [vue]webpack打包