一張圖完全搞懂MySQL的 explain
explain關鍵字能夠模擬MySQL優化器執行SQL語句,能夠很好的分析SQL語句或表結構的性能瓶頸。mysql
explain的用途
1. 表的讀取順序如何
2. 數據讀取操做有哪些操做類型
3. 哪些索引能夠使用
4. 哪些索引被實際使用
5. 表之間是如何引用
6. 每張表有多少行被優化器查詢
......
複製代碼
explain的執行效果
mysql> explain select * from subject where id = 1 \G
******************************************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: subject
partitions: NULL
type: const
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 4
ref: const
rows: 1
filtered: 100.00
Extra: NULL
******************************************************
複製代碼
explain包含的字段
1. id //select查詢的序列號,包含一組數字,表示查詢中執行select子句或操做表的順序
2. select_type //查詢類型
3. table //正在訪問哪一個表
4. partitions //匹配的分區
5. type //訪問的類型
6. possible_keys //顯示可能應用在這張表中的索引,一個或多個,但不必定實際使用到
7. key //實際使用到的索引,若是爲NULL,則沒有使用索引
8. key_len //表示索引中使用的字節數,可經過該列計算查詢中使用的索引的長度
9. ref //顯示索引的哪一列被使用了,若是可能的話,是一個常數,哪些列或常量被用於查找索引列上的值
10. rows //根據表統計信息及索引選用狀況,大體估算出找到所需的記錄所需讀取的行數
11. filtered //查詢的錶行佔表的百分比
12. Extra //包含不適合在其它列中顯示但十分重要的額外信息
複製代碼
圖片版
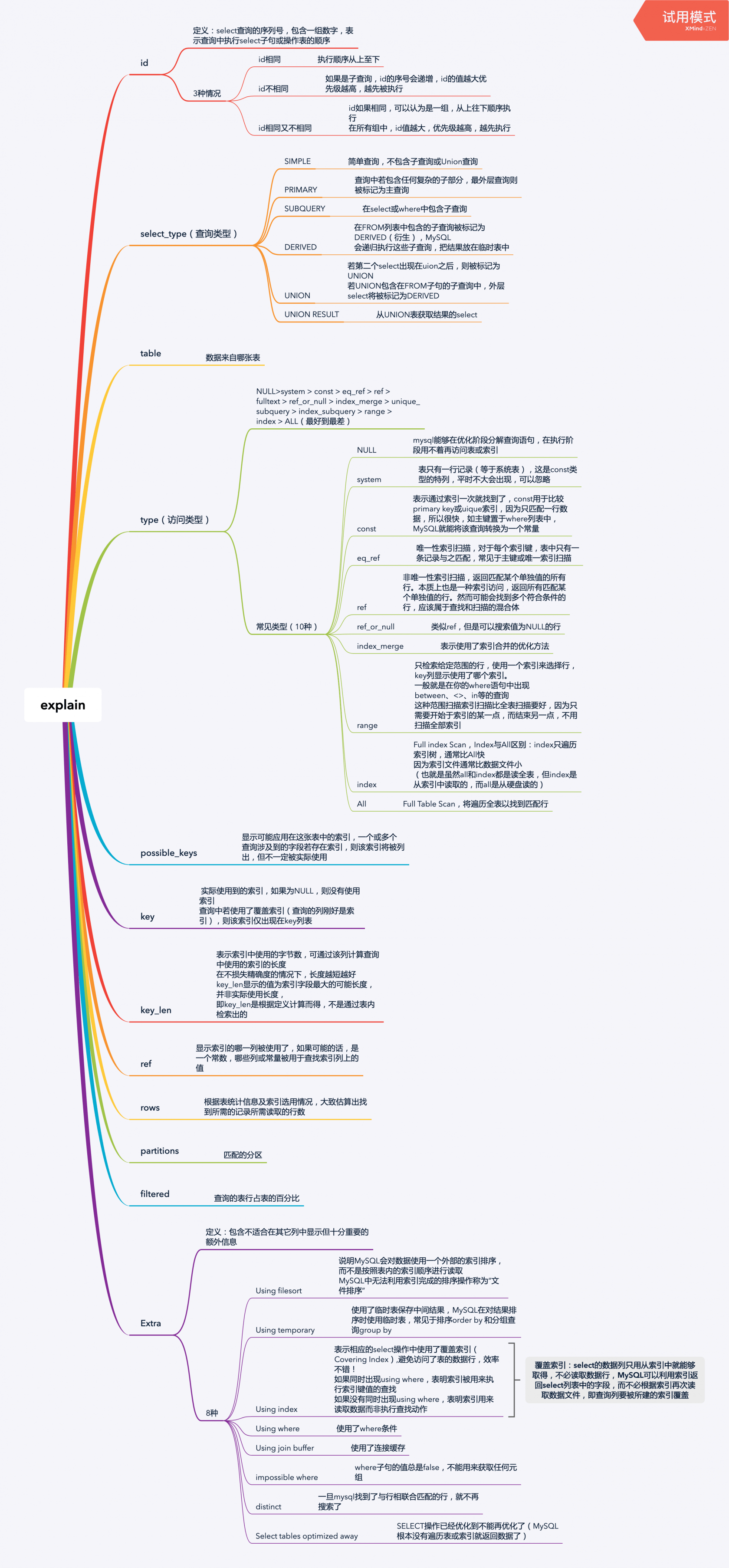
文字版
id字段
1. id相同
執行順序從上至下
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject,student_score,teacher where subject.id = student_id and subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;
讀取順序:subject > teacher > student_score
複製代碼

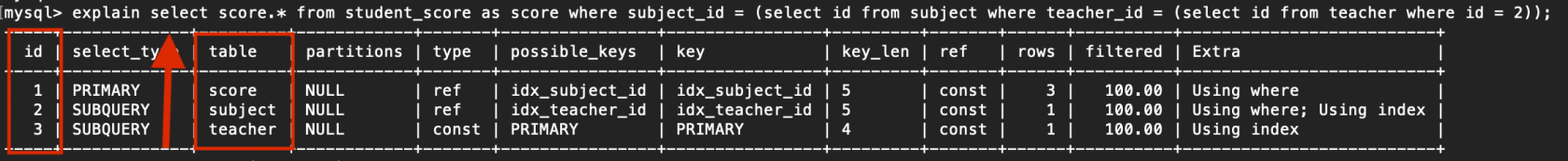
2. id不一樣
若是是子查詢,id的序號會遞增,id的值越大優先級越高,越先被執行
例子:
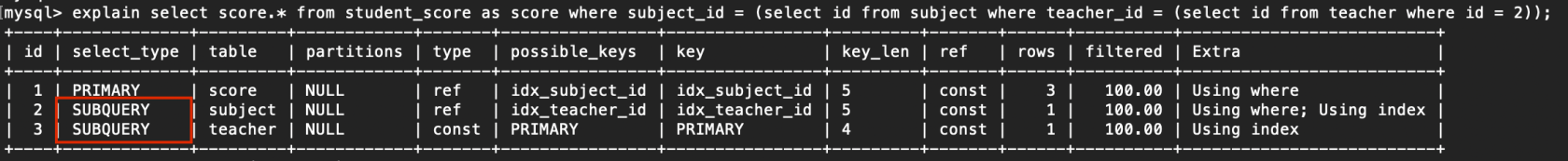
explain select score.* from student_score as score where subject_id = (select id from subject where teacher_id = (select id from teacher where id = 2));
讀取順序:teacher > subject > student_score
複製代碼
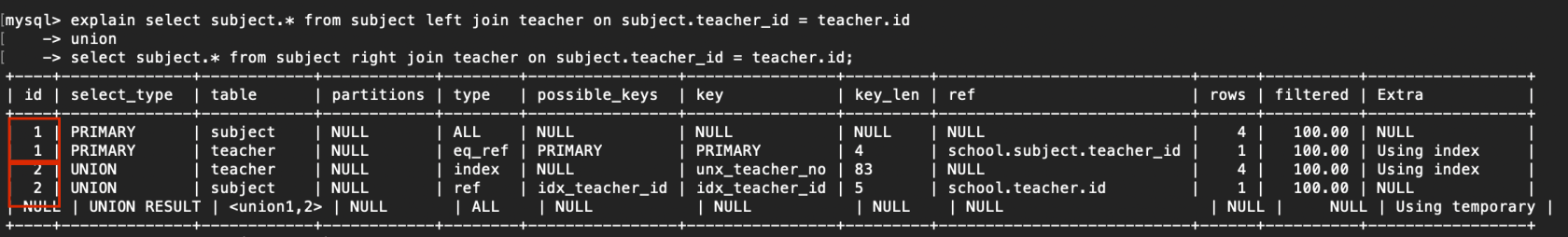
3. id相同又不一樣
id若是相同,能夠認爲是一組,從上往下順序執行
在全部組中,id值越大,優先級越高,越先執行
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject left join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id
-> union
-> select subject.* from subject right join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;
讀取順序:2.teacher > 2.subject > 1.subject > 1.teacher
複製代碼
select_type字段
1. SIMPLE
簡單查詢,不包含子查詢或Union查詢
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject,student_score,teacher where subject.id = student_id and subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;
複製代碼

2. PRIMARY
查詢中若包含任何複雜的子部分,最外層查詢則被標記爲主查詢
例子:
explain select score.* from student_score as score where subject_id = (select id from subject where teacher_id = (select id from teacher where id = 2));
複製代碼
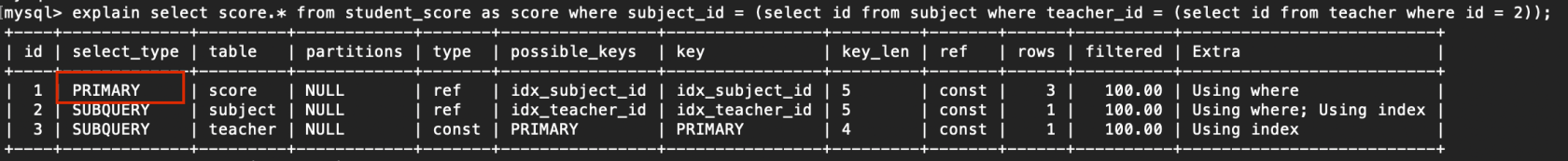
3. SUBQUERY
在select或where中包含子查詢
例子:
explain select score.* from student_score as score where subject_id = (select id from subject where teacher_id = (select id from teacher where id = 2));
複製代碼
4. DERIVED
在FROM列表中包含的子查詢被標記爲DERIVED(衍生),MySQL
會遞歸執行這些子查詢,把結果放在臨時表中
備註:
MySQL5.7+ 進行優化了,增長了derived_merge(派生合併),默認開啓,可加快查詢效率
複製代碼
5. UNION
若第二個select出如今uion以後,則被標記爲UNION
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject left join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id
-> union
-> select subject.* from subject right join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;
複製代碼
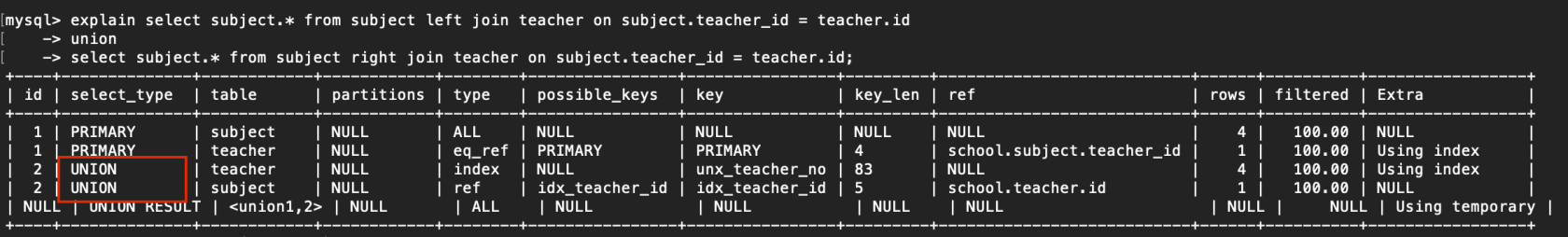
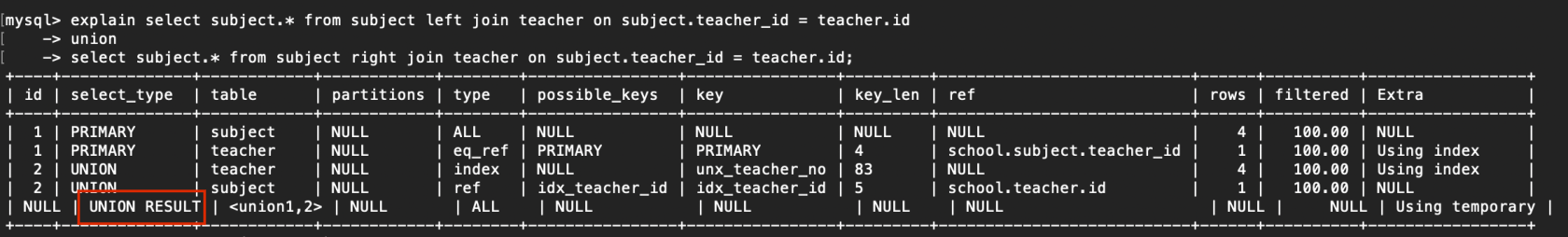
6. UNION RESULT
從UNION表獲取結果的select
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject left join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id
-> union
-> select subject.* from subject right join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;
複製代碼
type字段
NULL>system>const>eq_ref>ref>fulltext>ref_or_null>index_merge>unique_subquery>index_subquery>range>index>ALL //最好到最差
備註:掌握如下10種常見的便可
NULL>system>const>eq_ref>ref>ref_or_null>index_merge>range>index>ALL
複製代碼
1. NULL
MySQL可以在優化階段分解查詢語句,在執行階段用不着再訪問表或索引
例子:
explain select min(id) from subject;
複製代碼

2. system
表只有一行記錄(等於系統表),這是const類型的特列,平時不大會出現,能夠忽略
複製代碼
3. const
表示經過索引一次就找到了,const用於比較primary key或uique索引,由於只匹配一行數據,因此很快,如主鍵置於where列表中,MySQL就能將該查詢轉換爲一個常量
例子:
explain select * from teacher where teacher_no = 'T2010001';
複製代碼

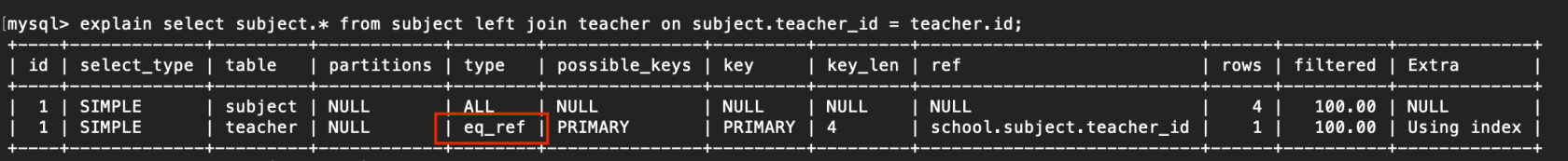
4. eq_ref
惟一性索引掃描,對於每一個索引鍵,表中只有一條記錄與之匹配,常見於主鍵或惟一索引掃描
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject left join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;
複製代碼
5. ref
非惟一性索引掃描,返回匹配某個單獨值的全部行
本質上也是一種索引訪問,返回全部匹配某個單獨值的行
然而可能會找到多個符合條件的行,應該屬於查找和掃描的混合體
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject,student_score,teacher where subject.id = student_id and subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;
複製代碼

6. ref_or_null
相似ref,可是能夠搜索值爲NULL的行
例子:
explain select * from teacher where name = 'wangsi' or name is null;
複製代碼

7. index_merge
表示使用了索引合併的優化方法
例子:
explain select * from teacher where id = 1 or teacher_no = 'T2010001' .
複製代碼

8. range
只檢索給定範圍的行,使用一個索引來選擇行,key列顯示使用了哪一個索引
通常就是在你的where語句中出現between、<>、in等的查詢。
例子:
explain select * from subject where id between 1 and 3;
複製代碼

9. index
Full index Scan,Index與All區別:index只遍歷索引樹,一般比All快
由於索引文件一般比數據文件小,也就是雖然all和index都是讀全表,但index是從索引中讀取的,而all是從硬盤讀的。
例子:
explain select id from subject;
複製代碼

10. ALL
Full Table Scan,將遍歷全表以找到匹配行
例子:
explain select * from subject;
複製代碼

table字段
數據來自哪張表
複製代碼
possible_keys字段
顯示可能應用在這張表中的索引,一個或多個
查詢涉及到的字段若存在索引,則該索引將被列出,但不必定被實際使用
複製代碼
key字段
實際使用到的索引,若是爲NULL,則沒有使用索引
查詢中若使用了覆蓋索引(查詢的列恰好是索引),則該索引僅出如今key列表
複製代碼
key_len字段
表示索引中使用的字節數,可經過該列計算查詢中使用的索引的長度
在不損失精確度的狀況下,長度越短越好
key_len顯示的值爲索引字段最大的可能長度,並不是實際使用長度
即key_len是根據定義計算而得,不是經過表內檢索出的
複製代碼
ref字段
顯示索引的哪一列被使用了,若是可能的話,是一個常數,哪些列或常量被用於查找索引列上的值
複製代碼
rows字段
根據表統計信息及索引選用狀況,大體估算出找到所需的記錄所需讀取的行數
複製代碼
partitions字段
匹配的分區
複製代碼
filtered字段
查詢的錶行佔表的百分比
複製代碼
Extra字段
包含不適合在其它列中顯示但十分重要的額外信息
複製代碼
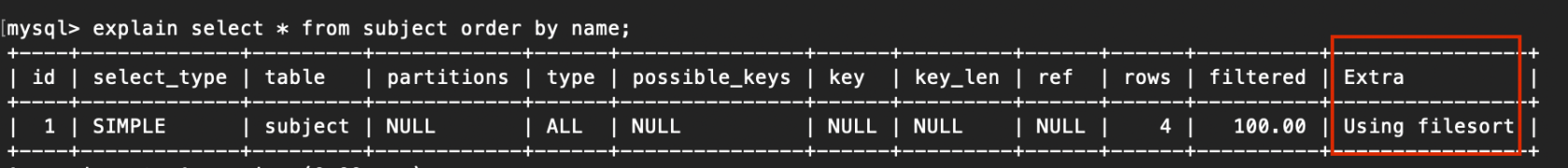
1. Using filesort
說明MySQL會對數據使用一個外部的索引排序,而不是按照表內的索引順序進行讀取
MySQL中沒法利用索引完成的排序操做稱爲「文件排序」
例子:
explain select * from subject order by name;
複製代碼
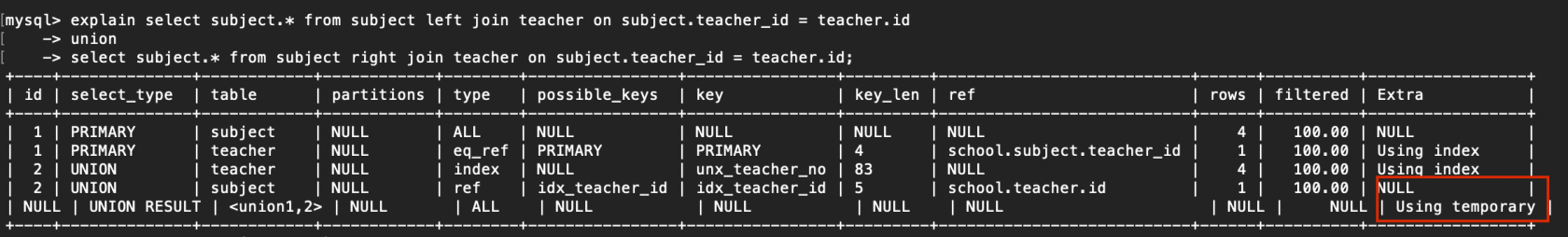
2. Using temporary
使用了臨時表保存中間結果,MySQL在對結果排序時使用臨時表,常見於排序order by 和分組查詢group by
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject left join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id
-> union
-> select subject.* from subject right join teacher on subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;
複製代碼
3. Using index
表示相應的select操做中使用了覆蓋索引(Covering Index),避免訪問了表的數據行,效率不錯!
若是同時出現using where,代表索引被用來執行索引鍵值的查找
若是沒有同時出現using where,代表索引用來讀取數據而非執行查找動做
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject,student_score,teacher where subject.id = student_id and subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;
備註:
覆蓋索引:select的數據列只用從索引中就可以取得,沒必要讀取數據行,MySQL能夠利用索引返回select列表中的字段,而沒必要根據索引再次讀取數據文件,即查詢列要被所建的索引覆蓋
複製代碼

4. Using where
使用了where條件
例子:
explain select subject.* from subject,student_score,teacher where subject.id = student_id and subject.teacher_id = teacher.id;
複製代碼

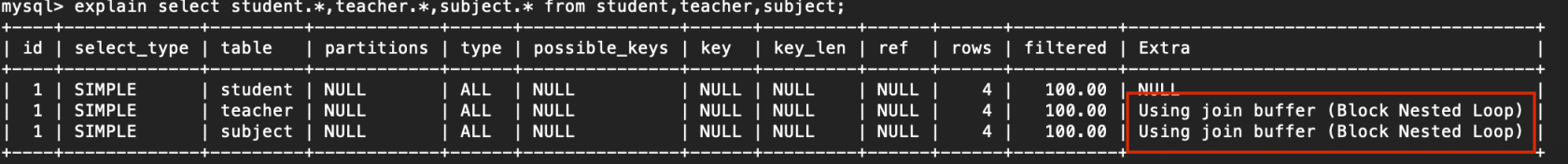
5. Using join buffer
使用了鏈接緩存
例子:
explain select student.*,teacher.*,subject.* from student,teacher,subject;
複製代碼
6. impossible where
where子句的值老是false,不能用來獲取任何元組
例子:
explain select * from teacher where name = 'wangsi' and name = 'lisi';
複製代碼

7. distinct
一旦mysql找到了與行相聯合匹配的行,就再也不搜索了
例子:
explain select distinct teacher.name from teacher left join subject on teacher.id = subject.teacher_id;
複製代碼

8. Select tables optimized away
SELECT操做已經優化到不能再優化了(MySQL根本沒有遍歷表或索引就返回數據了)
例子:
explain select min(id) from subject;
複製代碼

使用的數據表
create table subject(
-> id int(10) auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20),
-> teacher_id int(10),
-> primary key (id),
-> index idx_teacher_id (teacher_id));//學科表
create table teacher(
-> id int(10) auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20),
-> teacher_no varchar(20),
-> primary key (id),
-> unique index unx_teacher_no (teacher_no(20)));//教師表
create table student(
-> id int(10) auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20),
-> student_no varchar(20),
-> primary key (id),
-> unique index unx_student_no (student_no(20)));//學生表
create table student_score(
-> id int(10) auto_increment,
-> student_id int(10),
-> subject_id int(10),
-> score int(10),
-> primary key (id),
-> index idx_student_id (student_id),
-> index idx_subject_id (subject_id));//學生成績表
alter table teacher add index idx_name(name(20));//教師表增長名字普通索引
數據填充:
insert into student(name,student_no) values ('zhangsan','20200001'),('lisi','20200002'),('yan','20200003'),('dede','20200004');
insert into teacher(name,teacher_no) values('wangsi','T2010001'),('sunsi','T2010002'),('jiangsi','T2010003'),('zhousi','T2010004');
insert into subject(name,teacher_id) values('math',1),('Chinese',2),('English',3),('history',4);
insert into student_score(student_id,subject_id,score) values(1,1,90),(1,2,60),(1,3,80),(1,4,100),(2,4,60),(2,3,50),(2,2,80),(2,1,90),(3,1,90),(3,4,100),(4,1,40),(4,2,80),(4,3,80),(4,5,100);
複製代碼
相關文章
- 1. 一張圖完全搞懂MySQL的 explain
- 2. 一本完全搞懂MySQL索引優化EXPLAIN百科全書
- 3. 完全搞懂 MySQL 分區!
- 4. 完全搞懂MySQL分區
- 5. 一文完全搞懂MySQL分區
- 6. (轉)一張圖完全搞懂JavaScript的==運算
- 7. 一張圖完全搞懂 JavaScript 的 == 運算
- 8. 一張圖搞懂MySQL的索引失效
- 9. 一文完全搞懂MySQL索引
- 10. 兩張圖完全搞懂MyBatis的Mapper原理!
- 更多相關文章...
- • SQLite Explain(解釋) - SQLite教程
- • MySQL視圖簡介 - MySQL教程
- • 漫談MySQL的鎖機制
- • Tomcat學習筆記(史上最全tomcat學習筆記)
相關標籤/搜索
每日一句
-
每一个你不满意的现在,都有一个你没有努力的曾经。
歡迎關注本站公眾號,獲取更多信息
