What、Why、How?解讀Webpack官方文檔
What is Webpack?
Webpack具備Grunt、Gulp對於靜態資源自動化構建的能力,但更重要的是,Webpack彌補了requireJS在模塊化方面的缺陷,同時兼容AMD與CMD的模塊加載規範,具備更強大的JS模塊化的功能。javascript
所以我理解的Webpack,就是一個更出色的前端自動化構建工具、模塊化工具、資源管理工具。css
webpack is a module bundler. webpack takes modules with dependencies and generates static assets representing those modules.html
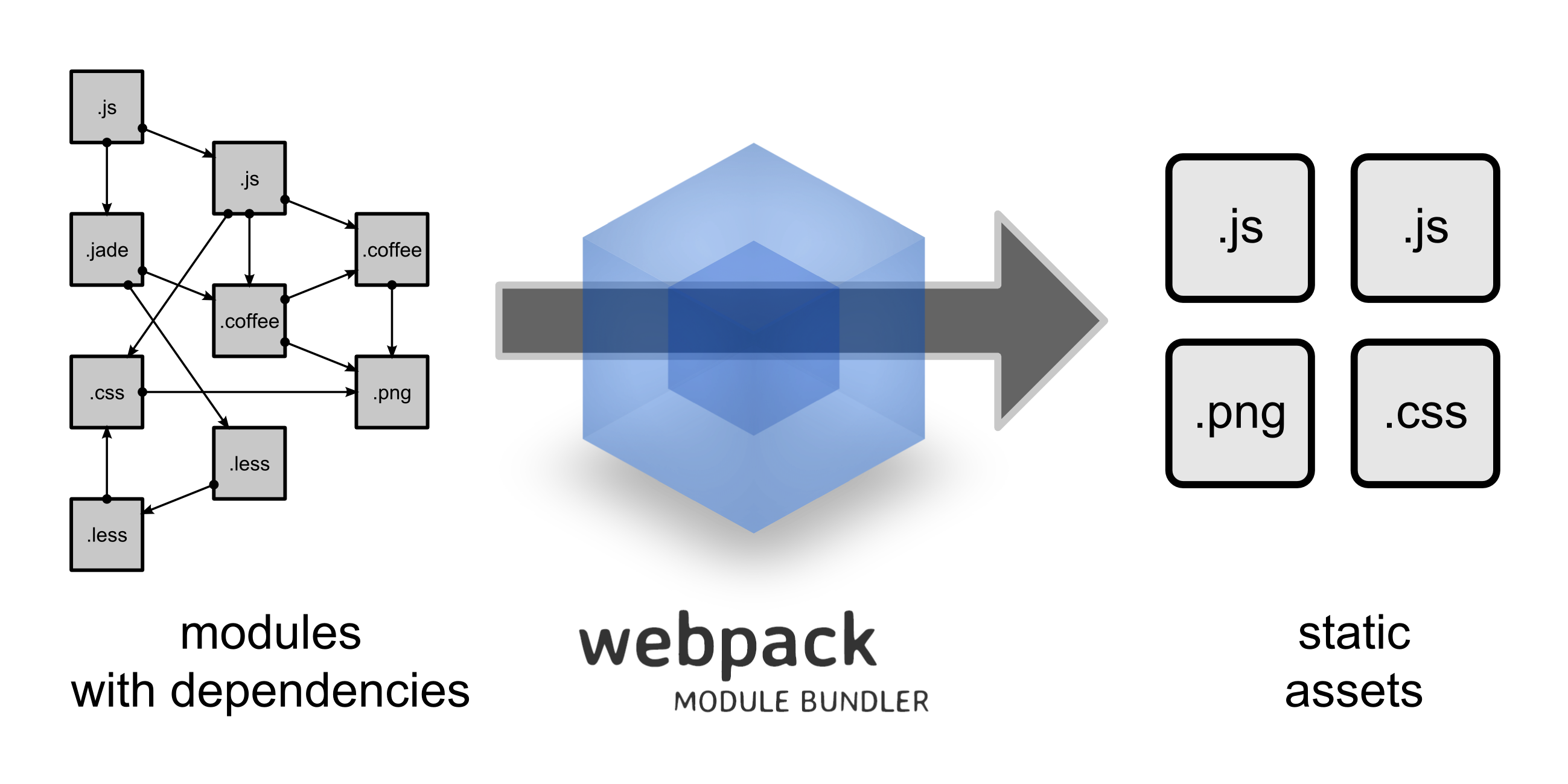
Why Webpack?
爲何選擇Webpack,兩點緣由。
一、前端須要模塊化:JS模塊化不只僅爲了提升代碼複用性,更是爲了讓資源文件更合理地進行緩存;前端
二、AMD與CMD規範日漸衰弱:緣由?ES6帶來了很強的模塊化語法糖。雖然ES6的更多語法糖讓JS可能失去了簡單的優點,在一些技術社區還偶爾看到一些反ES6的文章,但感受ES6仍然是將來發展的趨勢;java
module DBLayer {
export function query(s) { ... }
export function connection(..args) { ... }
}
import DBLayer.*;
module CanvasLib = require('http://../canvas.js');
import CanvasLib.{Triangle, rotate};
參考使用簡單的JavaScript,咱們爲何應該抵制ES6例子。node
固然,ES6,我以爲仍是將來的事情,尤爲是在China地盤要全面普及支持ES6的高級瀏覽器,真的比證實你媽是你媽還要困難。webpack
因此,我認爲,AMD跟CMD慢慢過期的緣由,是模塊化前端項目的發佈打包問題,requireJS跟seaJS都沒有一個很好的解決方案。下面配置文件是,我曾經作過的一個backbone的項目以requireJS作模塊化加載。項目初始階段還好,當隨着項目深刻,模塊切分得越細,最後發佈上線的時候,頁面對於JS的請求數量居然多達20個以上。大量的HTTPRequest形成的後果,不用多想,你們都知道。git
require.config({
//baseUrl: "scripts/vendor",
paths: {
underscore: '../vendor/underscore.min',
zepto: '../vendor/zepto.min',
backbone: '../vendor/backbone.min',
domReady: '../vendor/domReady',
template: '../vendor/template',
iscroll: '../vendor/iscroll/iscroll',
common: '../common/common'
},
shim: {
underscore: {
exports: '_'
},
zepto: {
exports: '$'
},
backbone: {
deps: ['underscore', 'zepto'],
exports: 'Backbone'
}
},
waitSeconds: 0
});
require([
'zepto',
'underscore',
'backbone',
'domReady',
'common',
'../controller/homeCtrl',
'../controller/fadeCtrl',
'../controller/mockCtrl'
],
function ($, _, backbone, domReady, common, homeCtrl, fadeCtrl, mockCtrl) {...}
爲了解決這個問題,引入的RequireJS的優化方案:r.js Optimizer。詳情:前端優化:RequireJS Optimizer 的使用和配置方法。github
({
name: "ptMain",
optimize: "uglify",//uglify
`out: "../build/ptMain-build.js",`
removeCombined: true,
paths: {
underscore: '../vendor/underscore.min',
zepto: '../vendor/zepto.min',
backbone: '../vendor/backbone.min',
domReady: '../vendor/domReady',
iscroll: '../vendor/iscroll/iscroll.min'
},
shim: {
underscore: {
exports: '_'
},
zepto: {
exports: '$'
},
backbone: {
deps: ['underscore', 'zepto'],
exports: 'Backbone'
}
}
});
r.js一樣能夠對各個js進行壓縮混淆優化,並最終在out配置中合併成一個JS文件,而後在頁面中調用。就是說,無論三七二十一,每一個頁面對應引用的JS,都會被打包成一個JS,但這樣的話,一個站點中多個頁面之間公用的JS模塊就沒法緩存起來了。web
說這麼多,其實就是說,Webpack把以上兩個問題解決了。
模塊化
全部資源都是模塊
你們能夠回頭看下Webpack官方實例圖,有一點不知道你們是否注意到:Webpack處理後,輸出的靜態文件只剩下js與png,而css、less、jade其餘的文件都合併到了js中。在Webpack當中,全部資源的都是模塊,模塊都須要經過AMD或者CMD規範加載,就像css樣式文件,再也不在HTML中以<link>標籤加載。


content.js
module.exports = "It works from content.js.";
entry.js
//樣式文件一樣以模塊方式引入
require("!style!css!./style.css");
//以CMD引入content.js
var content = require("./content.js");
function a() {
document.write(content);
};
a();
style.css
body {
background-color: yellow;
}
webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
entry: "./entry.js",
output: {
path: __dirname,
//打包輸出文件
filename: "bundle.js"
},
module: {
//loaders引入加載器
loaders: [
{ test: /\.css$/, loader: "style!css" }
]
}
};
bundle.js
/***/ function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
exports = module.exports = __webpack_require__(3)();
// imports
// module
exports.push([module.id, "body {\r\n background-color: yellow;\r\n}\r\n", ""]);
// exports
/***/ },
打包好的bundle,包含了樣式表在內的靜態資源,而index頁面下載bundle後,會將樣式還原到DOM當中。以下圖。
index.html
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript" src="bundle.js" charset="utf-8"></script>
</body>
</html>

代碼切分
代碼切分——抽取多個頁面公用模塊,打包成commonjs,便於緩存;
兩大重要概念:切分點(split point)與代碼塊(Chunk)
AMD and CommonJs specify different methods to load code on demand.Both are supported and act as split points
AMD與CMD定義引用模塊的入口就是切分點
All dependencies at a split point go into a new chunk
切分點定義中依賴的全部模塊,合起來就是一個代碼塊。說白了就是,一個頁面引用一個代碼塊
組織結構:build爲輸出結果目錄
邏輯結構
配置代碼
var path = require("path");
var CommonsChunkPlugin = require("../../node_modules/webpack/lib/optimize/CommonsChunkPlugin");
module.exports = {
entry: {
m1: './m1.js',
m2: './m2.js'
},
output: {
path: "build",
filename: '[name].bundle.js'
},
plugins: [
new CommonsChunkPlugin('common.js')
]
};
兼容AMD與CMD
CMD容許異步加載,寫法:
require.ensure(["module-a", "module-b"], function(require) {
var a = require("module-a");
// ...
});
Note: require.ensure only loads the modules, it doesn’t evaluate them.
注意:只下載,不執行
AMD寫法,與requireJS一致:
require(["module-a", "module-b"], function(a, b) {
// ...
});
Note: AMD require loads and evaluate the modules. In webpack modules are evaluated left to right.
注意:與CMD不同,AMD會下載並執行,執行順序從左到右
Note: It’s allowed to omit the callback.
注意:而且容許省略回調
不管是AMD與CMD,文件組織方式與模塊之間的邏輯都是同樣的
AMD示例:Github AMD example
CMD示例:Github CMD example


醜化
webpack提供插件UglifyJsPlugin,能夠優化(支持壓縮、混淆)代碼。插件引用方法詳細,請參照。
其中混淆配置是值得注意的,因爲AMD中的引用變量或方法名稱混淆容易形成錯誤,所以混淆配置能夠控制配置變量不被混淆。
A specific configuration is about mangling variable names. By default the mangle option is false. But you can say to the plugin avoid mangling a variable name passing a except list:
配置如下列表,在混淆代碼時,如下配置的變量,不會被混淆
new webpack.optimize.UglifyJsPlugin({
mangle: {
except: ['$super', '$', 'exports', 'require']
}
})
以上變量‘$super’, ‘$’, ‘exports’ or ‘require’,不會被混淆
Example:Github uglify example
var UglifyJsPlugin = require("../../node_modules/webpack/lib/optimize/UglifyJsPlugin");
module.exports = {
entry: "./entry.js",
output: {
path: __dirname,
filename: "bundle.js",
},
plugins: [
//使用醜化js插件
new UglifyJsPlugin({
compress: {
warnings: false
},
mangle: {
except: ['$scope', '$']
}
})
]
};
entry.js
define("entry", function () {
//變量 iabcdef 已引用,混淆
var iabcdef = 11;
//變量 $scope 已引用,但不混淆
var $scope = "scope";
document.write("entry module" + iabcdef);
document.write($scope);
//變量 ixzy 未被引用,剔除
var ixzy = 3241;
});
版本控制
對於靜態資源的版本控制,目前微信項目採起辦法是版本號做爲請求參數,版本號爲發佈日期,但有兩個問題:
一、更新版本時,CDN不能及時更新;
二、沒有發生變動的文件也被賦上新版本
Webpack的作法是,生成hash,區分文件。
Compute a hash of all chunks and add it.
生成全部代碼塊的hash
配置方法
//全部代碼塊添加hash
module.exports = {
entry: "./entry.js",
output: {
path: "assets/[hash]/",
publicPath: "assets/[hash]/",
filename: "bundle.js"
}
};
生成結果

Compute a hash per chunk and add it.
生成單個代碼塊文件的hash
配置方法
//單個代碼塊添加hash
module.exports = {
entry: "./entry.js",
output: {
path: "build/",
publicPath: "build/",
chunkFilename: "[id].[hash].bundle.js",
filename: "output.[hash].bundle.js",
}
};
How to use?
安裝
全局安裝,在任意目錄,輸入如下命令
$ npm install webpack -g
僅在項目在中安裝,切換到項目根目錄,輸入如下命令
$ npm install webpack --save-dev
檢查安裝成功後,顯示以下。
$ webpack -v

加載插件(Plugin)
引用項目根目錄node_modules
var path = require("path");
var CommonsChunkPlugin = require("../../node_modules/webpack/lib/optimize/CommonsChunkPlugin");
module.exports = {
entry: {
m1: './m1.js',
m2: './m2.js'
},
output: {
path: "build",
filename: '[name].bundle.js'
},
plugins: [
//引用插件
new CommonsChunkPlugin('common.js')
]
};
加載加載器(Loaders)
經過加載器能夠加載不一樣的資源文件進去各類操做,例如CoffeeScript及JSX……
安裝加載器命令
$ npm install xxx-loader --save
或
$ npm install xxx-loader --save-dev
加載器應用方法有3種:
explicit in the require statement (經過require語句,顯示引用)
configured via configuration (經過configuration來配置)
configured via CLI (經過CLI配置)
引入方法以下:
require("./loader!./dir/file.txt");
// => uses the file "loader.js" in the current directory to transform// "file.txt" in the folder "dir". //「!」是連接器,連接各個加載器及文件,./loader!代表loader有明確地址
require("jade!./template.jade");
// => uses the "jade-loader" (that is installed from npm to "node_modules")// to transform the file "template.jade" //jade-laoder,能夠簡寫爲jade,而且jade加載器須要安裝在「node_modules」
require("!style!css!less!bootstrap/less/bootstrap.less");
// => the file "bootstrap.less" in the folder "less" in the "bootstrap"// module (that is installed from github to "node_modules") is// transformed by the "less-loader". The result is transformed by the// "css-loader" and then by the "style-loader". //同時使用style,css,less三個加載器,並使用「!」做爲連接,對應文件時bootstrap.less
配置方法以下:
{
module: {
loaders: [
{ test: /\.jade$/, loader: "jade" },
// => "jade" loader is used for ".jade" files
{ test: /\.css$/, loader: "style!css" },
// => "style" and "css" loader is used for ".css" files
// Alternative syntax:
{ test: /\.css$/, loaders: ["style", "css"] },
]
}
}
- 1. Oozie — What Why and How
- 2. GO TESTING;HOW,WHAT,WHY
- 3. Spinnaker第一節-What、Why、How
- 4. kafka官方文檔解讀
- 5. 白板編程淺談——Why, What, How
- 6. Web性能優化:What? Why? How?
- 7. 3W法—what,why,how的運用
- 8. gRPC實戰--gRPC簡介:why,what,how?
- 9. 關於跨域的what,why,how
- 10. ***Research(科學研究) about what,how,and why***
- 更多相關文章...
- • WSDL 文檔 - WSDL 教程
- • XSL-FO 文檔 - XSL-FO 教程
- • JDK13 GA發佈:5大特性解讀
- • SpringBoot中properties文件不能自動提示解決方法
-
每一个你不满意的现在,都有一个你没有努力的曾经。