SSM (十五) 樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖的實際應用
前言
隨着互聯網的興起,如今三高(高可用、高性能、高併發)項目是愈來愈流行。java
本次來談談高併發。首先假設一個業務場景:數據庫中有一條數據,須要獲取到當前的值,在當前值的基礎上+10,而後再更新回去。
若是此時有兩個線程同時併發處理,第一個線程拿到數據是10,+10=20更新回去。第二個線程本來是要在第一個線程的基礎上再+20=40,結果因爲併發訪問取到更新前的數據爲10,+20=30。git
這就是典型的存在中間狀態,致使數據不正確。來看如下的例子:github
併發所帶來的問題
和上文提到的相似,這裏有一張price表,表結構以下:redis
CREATE TABLE `price` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主鍵',
`total` decimal(12,2) DEFAULT '0.00' COMMENT '總值',
`front` decimal(12,2) DEFAULT '0.00' COMMENT '消費前',
`end` decimal(12,2) DEFAULT '0.00' COMMENT '消費後',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1268 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8複製代碼
我這裏寫了一個單測:就一個主線程,循環100次,每次把front的值減去10,再寫入一次流水記錄,正常狀況是寫入的每條記錄都會每次減去10。sql
/** * 單線程消費 */
@Test
public void singleCounsumerTest1(){
for (int i=0 ;i<100 ;i++){
Price price = priceMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
int ron = 10 ;
price.setFront(price.getFront().subtract(new BigDecimal(ron)));
price.setEnd(price.getEnd().add(new BigDecimal(ron)));
price.setTotal(price.getFront().add(price.getEnd()));
priceMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(price) ;
price.setId(null);
priceMapper.insertSelective(price) ;
}
}複製代碼
執行結果以下:數據庫
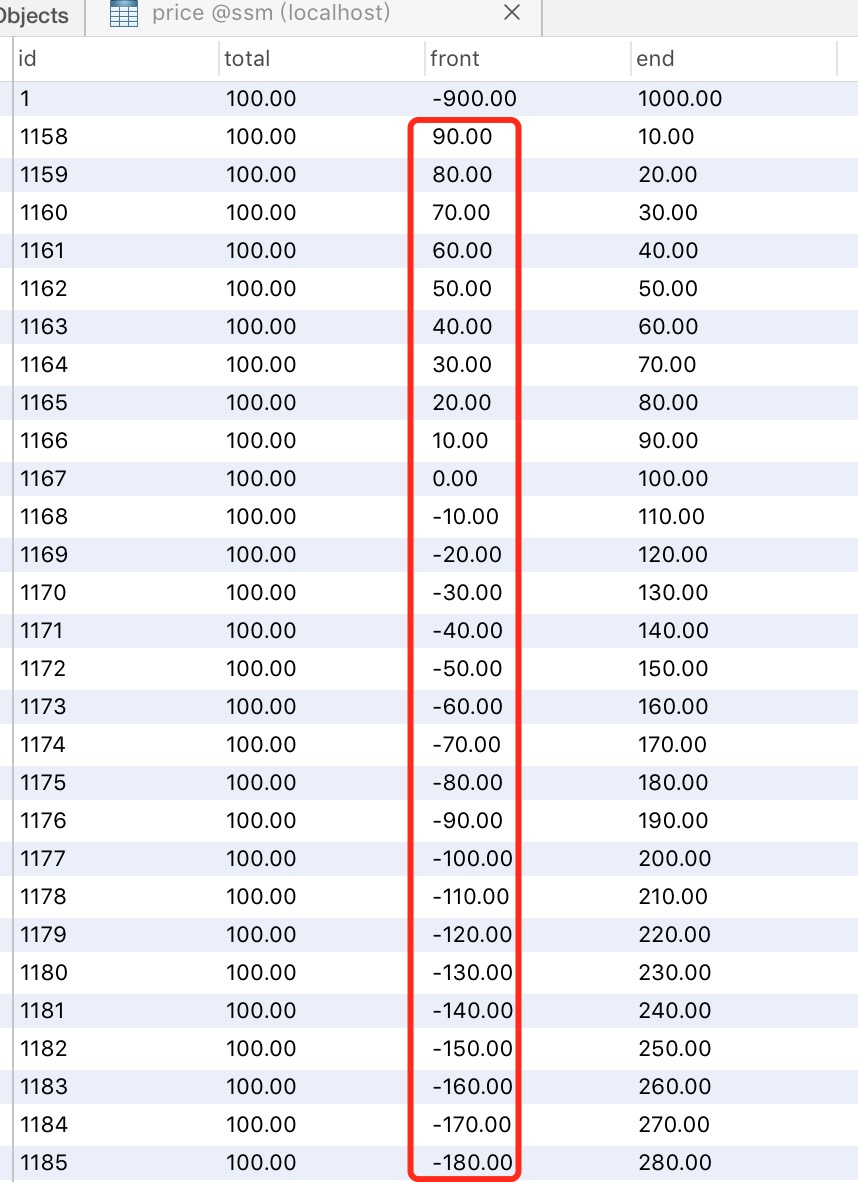
能夠看到確實是每次都遞減10。
可是若是是多線程的狀況下會是如何呢:多線程
我這裏新建了一個
PriceController併發
/** * 線程池 無鎖 * @param redisContentReq * @return */
@RequestMapping(value = "/threadPrice",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public BaseResponse<NULLBody> threadPrice(@RequestBody RedisContentReq redisContentReq){
BaseResponse<NULLBody> response = new BaseResponse<NULLBody>() ;
try {
for (int i=0 ;i<10 ;i++){
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Price price = priceMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
int ron = 10 ;
price.setFront(price.getFront().subtract(new BigDecimal(ron)));
price.setEnd(price.getEnd().add(new BigDecimal(ron)));
priceMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(price) ;
price.setId(null);
priceMapper.insertSelective(price) ;
}
});
config.submit(t);
}
response.setReqNo(redisContentReq.getReqNo());
response.setCode(StatusEnum.SUCCESS.getCode());
response.setMessage(StatusEnum.SUCCESS.getMessage());
}catch (Exception e){
logger.error("system error",e);
response.setReqNo(response.getReqNo());
response.setCode(StatusEnum.FAIL.getCode());
response.setMessage(StatusEnum.FAIL.getMessage());
}
return response ;
}複製代碼
其中爲了節省資源使用了一個線程池:app
@Component
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
private static final int MAX_SIZE = 10 ;
private static final int CORE_SIZE = 5;
private static final int SECOND = 1000;
private ThreadPoolExecutor executor ;
public ThreadPoolConfig(){
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_SIZE,MAX_SIZE,SECOND, TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()) ;
}
public void submit(Thread thread){
executor.submit(thread) ;
}
}複製代碼
關於線程池的使用從此會仔細探討。這裏就簡單理解爲有10個線程併發去處理上面單線程的邏輯,來看看結果怎麼樣:dom
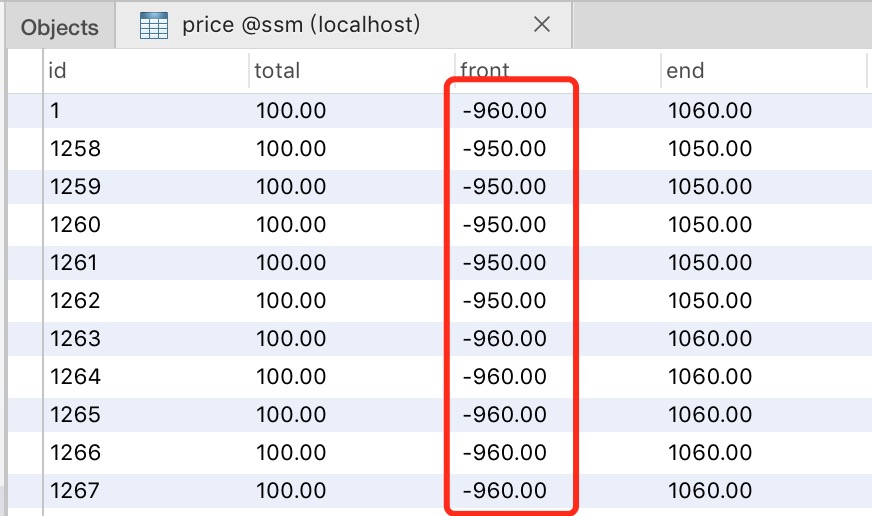
會看到明顯的數據錯誤,致使錯誤的緣由天然就是有線程讀取到了中間狀態進行了錯誤的更新。
進而有了如下兩種解決方案:悲觀鎖和樂觀鎖。
悲觀鎖
簡單理解下悲觀鎖:當一個事務鎖定了一些數據以後,只有噹噹前鎖提交了事務,釋放了鎖,其餘事務才能得到鎖並執行操做。
使用方式以下:
首先要關閉MySQL的自動提交:set autocommit = 0;
bigen --開啓事務
select id, total, front, end from price where id=1 for update
insert into price values(?,?,?,?,?)
commit --提交事務複製代碼
這裏使用select for update的方式利用數據庫開啓了悲觀鎖,鎖定了id=1的這條數據(注意:這裏除非是使用了索引會啓用行級鎖,否則是會使用表鎖,將整張表都鎖住。)。以後使用commit提交事務並釋放鎖,這樣下一個線程過來拿到的就是正確的數據。
悲觀鎖通常是用於併發不是很高,而且不容許髒讀等狀況。可是對數據庫資源消耗較大。
樂觀鎖
那麼有沒有性能好,支持的併發也更多的方式呢?
那就是樂觀鎖。
樂觀鎖是首先假設數據衝突不多,只有在數據提交修改的時候才進行校驗,若是衝突了則不會進行更新。
一般的實現方式增長一個version字段,爲每一條數據加上版本。每次更新的時候version+1,而且更新時候帶上版本號。實現方式以下:
新建了一張price_version表:
CREATE TABLE `price_version` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主鍵',
`total` decimal(12,2) DEFAULT '0.00' COMMENT '總值',
`front` decimal(12,2) DEFAULT '0.00' COMMENT '消費前',
`end` decimal(12,2) DEFAULT '0.00' COMMENT '消費後',
`version` int(11) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '併發版本控制',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1268 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8複製代碼
更新數據的SQL:
<update id="updateByVersion" parameterType="com.crossoverJie.pojo.PriceVersion">
UPDATE price_version
SET front = #{front,jdbcType=DECIMAL},
version= version + 1
WHERE id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
AND version = #{version,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</update>複製代碼
調用方式:
/** * 線程池,樂觀鎖 * @param redisContentReq * @return */
@RequestMapping(value = "/threadPriceVersion",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public BaseResponse<NULLBody> threadPriceVersion(@RequestBody RedisContentReq redisContentReq){
BaseResponse<NULLBody> response = new BaseResponse<NULLBody>() ;
try {
for (int i=0 ;i<3 ;i++){
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
PriceVersion priceVersion = priceVersionMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
int ron = new Random().nextInt(20);
logger.info("本次消費="+ron);
priceVersion.setFront(new BigDecimal(ron));
int count = priceVersionMapper.updateByVersion(priceVersion);
if (count == 0){
logger.error("更新失敗");
}else {
logger.info("更新成功");
}
}
});
config.submit(t);
}
response.setReqNo(redisContentReq.getReqNo());
response.setCode(StatusEnum.SUCCESS.getCode());
response.setMessage(StatusEnum.SUCCESS.getMessage());
}catch (Exception e){
logger.error("system error",e);
response.setReqNo(response.getReqNo());
response.setCode(StatusEnum.FAIL.getCode());
response.setMessage(StatusEnum.FAIL.getMessage());
}
return response ;
}複製代碼
處理邏輯:開了三個線程生成了20之內的隨機數更新到front字段。
當調用該接口時日誌以下:
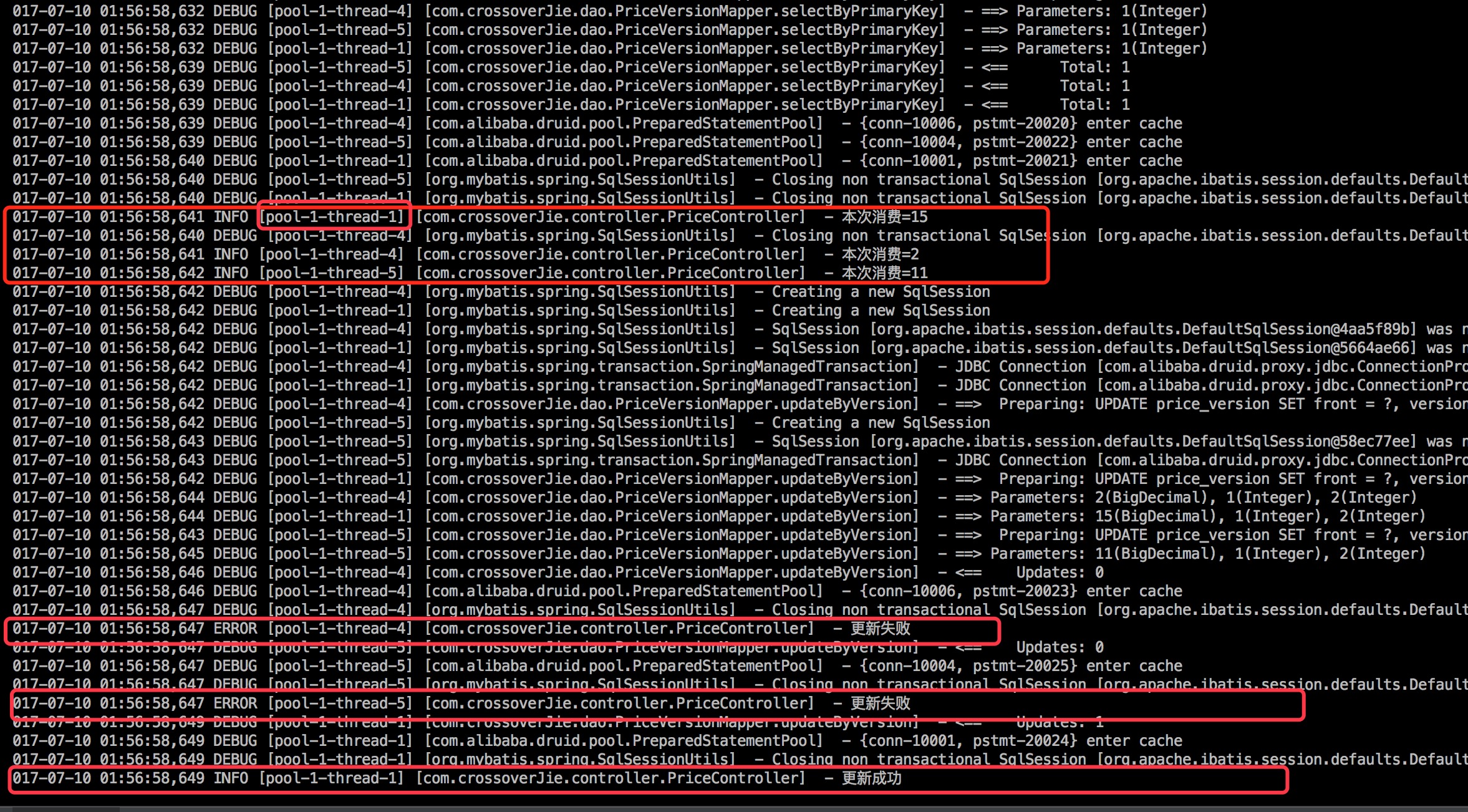
能夠看到線程一、四、5分別生成了15,2,11三個隨機數。最後線程四、5都更新失敗了,只有線程1更新成功了。
查看數據庫:

發現也確實是更新的15。
樂觀鎖在實際應用相對較多,它能夠提供更好的併發訪問,而且數據庫開銷較少,可是有可能存在髒讀的狀況。
總結
以上兩種各有優劣,你們能夠根據具體的業務場景來判斷具體使用哪一種方式來保證數據的一致性。
我的博客地址:crossoverjie.top。

- 1. 關於樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖的實際應用
- 2. 樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖的實際應用
- 3. 樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖
- 4. 悲觀鎖與樂觀鎖
- 5. 悲觀鎖與樂觀鎖(CAS實現)
- 6. 樂觀鎖&悲觀鎖
- 7. hibernate 樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖使用
- 8. MySQL鎖(4):樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖
- 9. MySQL鎖-樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖
- 更多相關文章...
- • Hibernate悲觀鎖 - Hibernate教程
- • Hibernate樂觀鎖 - Hibernate教程
- • 漫談MySQL的鎖機制
- • TiDB 在摩拜單車在線數據業務的應用和實踐
-
每一个你不满意的现在,都有一个你没有努力的曾经。
- 1. Appium入門
- 2. Spring WebFlux 源碼分析(2)-Netty 服務器啓動服務流程 --TBD
- 3. wxpython入門第六步(高級組件)
- 4. CentOS7.5安裝SVN和可視化管理工具iF.SVNAdmin
- 5. jedis 3.0.1中JedisPoolConfig對象缺少setMaxIdle、setMaxWaitMillis等方法,問題記錄
- 6. 一步一圖一代碼,一定要讓你真正徹底明白紅黑樹
- 7. 2018-04-12—(重點)源碼角度分析Handler運行原理
- 8. Spring AOP源碼詳細解析
- 9. Spring Cloud(1)
- 10. python簡單爬去油價信息發送到公衆號
- 1. 關於樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖的實際應用
- 2. 樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖的實際應用
- 3. 樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖
- 4. 悲觀鎖與樂觀鎖
- 5. 悲觀鎖與樂觀鎖(CAS實現)
- 6. 樂觀鎖&悲觀鎖
- 7. hibernate 樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖使用
- 8. MySQL鎖(4):樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖
- 9. MySQL鎖-樂觀鎖與悲觀鎖